Chemical Engineering: Courses, Specializations, Careers
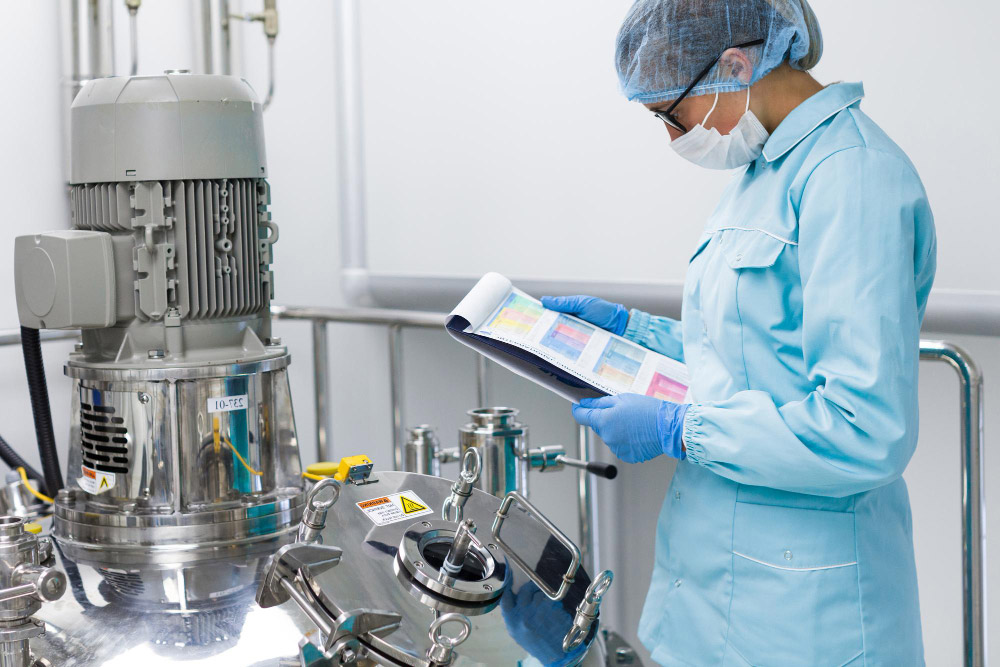
Chemical Engineering is a specialized field of study that combines principles of chemistry, physics, biology, and mathematics to design, develop, and optimize processes involving the transformation of raw materials into valuable products. This discipline focuses on finding innovative solutions to various challenges in industries such as manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, energy, and environmental sustainability.
Chemical Engineering Course Highlights
- Rigorous curriculum: Chemical Engineering courses provide a comprehensive understanding of core concepts and advanced principles in the field.
- Hands-on experience: Students engage in practical laboratory sessions, research projects, and industrial internships to gain real-world experience.
- Interdisciplinary approach: The curriculum integrates knowledge from various disciplines, including chemistry, physics, biology, and mathematics.
- Cutting-edge technology: Students have access to state-of-the-art equipment and software used in chemical engineering research and industry.
- Collaborative learning: Group projects and teamwork opportunities foster collaboration and enhance problem-solving skills.
- Industry connections: Many institutions have strong partnerships with leading companies, providing students with networking and job placement opportunities.
Why Choose Chemical Engineering?
Choosing a Chemical Engineering course can open up numerous opportunities and offer several advantages. Here are some compelling reasons to pursue Chemical Engineering:
- Vast career prospects: Chemical Engineering graduates have diverse career options in industries such as oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, environmental engineering, and materials science.
- Impactful contributions: Chemical engineers play a crucial role in developing sustainable solutions, improving energy efficiency, and mitigating environmental impacts.
- Lucrative salaries: Chemical engineers often receive attractive salary packages due to the high demand for their specialized skills.
- Continuous innovation: This field constantly evolves, presenting new challenges and opportunities for innovation and research.
- Global relevance: Chemical engineering knowledge and skills are in demand worldwide, offering opportunities for international work experience and collaborations.
Types of Chemical Engineering Courses
Chemical Engineering courses are available at various levels, including undergraduate (Bachelors), postgraduate (Masters), and doctoral (Ph.D.). Additionally, there are specialized courses and certifications available for professionals seeking to enhance their expertise in specific areas of Chemical Engineering.
List of Popular Chemical Engineering Specializations
Chemical Engineering offers several specialization options for students to focus their studies and expertise. Some popular specializations include:
- Process Engineering
- Biochemical Engineering
- Environmental Engineering
- Polymer Engineering
- Energy Engineering
- Pharmaceutical Engineering
- Nanotechnology and Materials Engineering
Learning Outcomes
Upon completion of a Chemical Engineering course, students can expect to:
- Gain a strong foundation in fundamental principles of chemical engineering, including mass and energy balances, fluid mechanics, thermodynamics, and reaction kinetics.
- Develop problem-solving and critical thinking skills to address complex engineering challenges.
- Acquire knowledge of various chemical engineering processes and techniques used in different industries.
- Apply theoretical concepts to practical scenarios through laboratory experiments and industrial projects.
- Gain proficiency in using software tools and technologies relevant to the field of chemical engineering.
- Develop effective communication and teamwork skills necessary for successful collaboration in a professional environment.
Course Outlines
Chemical Engineering courses typically cover a wide range of subjects to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of the field. Some common course topics include:
- Chemical Reaction Engineering
- Process Design and Optimization
- Heat and Mass Transfer
- Separation Processes
- Thermodynamics
- Fluid Mechanics
- Process Control and Instrumentation
- Chemical Kinetics
- Engineering Mathematics
- Safety and Environmental Engineering
Scope
The scope of Chemical Engineering is vast, with opportunities available in various industries and research institutions. Chemical engineers are involved in designing and optimizing processes, developing new materials, conducting research, managing projects, and ensuring environmental sustainability. They can work in sectors such as manufacturing, oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, energy production, environmental consulting, and academic institutions.
Job Outlook
The job outlook for Chemical Engineering graduates is promising, with a steady demand for skilled professionals in various sectors. The increasing focus on sustainable practices, renewable energy, and environmental regulations has created new opportunities for chemical engineers. They can find employment in roles such as process engineer, research scientist, project manager, quality control analyst, environmental engineer, and technical consultant.
Required Skillset for Chemical Engineering
To excel in Chemical Engineering, students should possess a strong set of skills and knowledge. Some essential skills for chemical engineers include:
- Strong analytical and problem-solving abilities
- Proficiency in mathematics and scientific principles
- Excellent communication and presentation skills
- Attention to detail and precision in experimental work
- Ability to work effectively in teams and collaborate with colleagues
- Knowledge of computer-aided design (CAD) software and programming languages
- Understanding of safety protocols and regulations in chemical processes
- Adaptability and willingness to learn new technologies and methodologies
Chemical Engineering Career Options and Job Prospects
Chemical Engineering graduates have a wide range of career options to explore. Some popular career paths include:
- Process Engineer: Designing and optimizing industrial processes to improve efficiency and productivity.
- Research Scientist: Conducting experiments, analyzing data, and developing new technologies in research institutions.
- Project Manager: Overseeing and managing engineering projects from conception to completion.
- Quality Control Analyst: Ensuring product quality and adherence to safety standards in manufacturing processes.
- Environmental Engineer: Developing solutions to minimize the environmental impact of chemical processes.
- Technical Consultant: Providing expertise and guidance to companies on process improvement and optimization.
Chemical Engineering Minimum Qualification Required
To pursue a degree in Chemical Engineering, the minimum qualification required is typically a high school diploma or equivalent qualification. However, admission to reputable institutions often requires meeting specific academic criteria, including a strong background in mathematics, physics, and chemistry. Graduate programs may have additional requirements such as a relevant undergraduate degree and standardized test scores (e.g., GRE).
Courses After Chemical Engineering
After completing a degree in Chemical Engineering, individuals can pursue further education or specialization to enhance their career prospects. Some common options include:
- Master's in Chemical Engineering: A postgraduate degree that provides advanced knowledge and specialization in specific areas of Chemical Engineering.
- MBA: Many chemical engineers opt for an MBA to develop management and business skills, opening up opportunities in leadership roles.
- Research or Ph.D. Programs: Those interested in research and academia can pursue a doctoral degree to contribute to the advancement of Chemical Engineering knowledge.
Challenges
Chemical Engineering education and practice come with certain challenges that students and professionals may encounter:
- Complex coursework: The technical nature of Chemical Engineering subjects requires dedication and hard work to grasp the concepts fully.
- Safety considerations: Chemical processes involve inherent risks, so adherence to safety protocols is of utmost importance.
- Continuous learning: The field evolves rapidly, necessitating ongoing learning and keeping up with emerging technologies and practices.
- Environmental concerns: Chemical engineers must address sustainability and environmental impact issues, requiring innovative and eco-friendly solutions.
Limitations
While Chemical Engineering offers numerous opportunities, it also has certain limitations:
- High level of competition: The field attracts a significant number of students, leading to increased competition for jobs and research positions.
- Technological advancements: Keeping up with the latest technologies and tools is essential, as outdated knowledge may limit career prospects.
- Specialized nature: Chemical Engineering may limit job prospects to specific industries, requiring individuals to be adaptable and open to diverse opportunities.
Emerging Trends
The field of Chemical Engineering is influenced by various emerging trends, including:
- Green and sustainable processes: The industry is increasingly focusing on developing eco-friendly and sustainable processes to minimize environmental impact.
- Biotechnology integration: Chemical Engineering is intersecting with biotechnology, leading to advancements in areas such as biofuels, bioplastics, and pharmaceuticals.
- Process automation and digitalization: Automation, data analytics, and artificial intelligence are revolutionizing process control and optimization in chemical plants.
- Energy storage and renewable energy: Chemical engineers are actively involved in developing efficient energy storage systems and exploring renewable energy sources.
FAQs about Chemical Engineering
-
What is a Chemical Engineering Course?
A Chemical Engineering Course is an academic program that covers the principles of chemistry, physics, and mathematics applied to the design, analysis, and optimization of processes involved in the production or use of chemicals and biochemicals.
-
Why should I choose a Chemical Engineering Course?
A Chemical Engineering Course offers a plethora of opportunities in various industries such as energy, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and more. The course provides a comprehensive understanding of the crucial aspects of these industries, opening doors for innovation and process optimization.
-
What are the different types of Chemical Engineering Courses?
There are several types of Chemical Engineering Courses, including Bachelor of Science in Chemical Engineering, Master of Science in Chemical Engineering, Doctor of Philosophy in Chemical Engineering, and several Diploma and Certificate Courses in specific areas of Chemical Engineering.
-
What are some popular specializations in Chemical Engineering?
Popular specializations in Chemical Engineering include Petrochemical Engineering, Biochemical Engineering, Process Engineering, Environmental Chemical Engineering, and Materials Engineering.
-
What learning outcomes can I expect from a Chemical Engineering Course?
The Chemical Engineering Course aims to equip learners with an in-depth understanding of fundamental and advanced principles of chemical engineering. It also provides hands-on experience through lab sessions and internships, fosters research skills, and encourages ethical considerations in practice.
-
What job prospects are available for Chemical Engineering graduates?
Job prospects for Chemical Engineering graduates are vast and promising. They can find opportunities in various roles such as Process Engineer, Chemical Equipment Engineer, Production Engineer, Research Scientist, and Quality Control Engineer in industries like energy, pharmaceuticals, and more.
-
What skills are required to succeed in Chemical Engineering?
Key skills required in Chemical Engineering include a strong understanding of chemical engineering principles, proficiency in mathematics and science, problem-solving and analytical abilities, creativity, teamwork, and good communication skills.
-
What are the minimum qualifications required for a Chemical Engineering Course?
The minimum qualification for a Bachelor's in Chemical Engineering is a high school diploma with a focus on mathematics and science. For a Master's, a bachelor's degree in chemical engineering or a related field is required. For Ph.D. programs, a master's degree, along with a strong research proposal, is typically required.
-
What are some challenges and limitations of Chemical Engineering?
Challenges and limitations in Chemical Engineering include the complexity of the subject matter, the need for continual learning due to rapidly evolving technology, and the potential environmental impact of chemical processes.
-
What are the emerging trends in Chemical Engineering?
Emerging trends in Chemical Engineering include green and sustainable engineering, bioengineering and biotechnology, and nanotechnology. These trends focus on developing environmentally friendly processes, applying engineering principles to biological processes, and working at the molecular level to create new materials and processes, respectively.
Meta Description: "Discover the world of Chemical Engineering with detailed courses, specializations, career options, and essential skills. Explore this comprehensive guide now!"
Engineering Topics