Government of Nepal Teacher Service Commission Teacher Licensing Curriculum for Secondary Level (Grade 9-12), 2075
First Paper: English 65 marks
Introduction
This curriculum is designed with the view to assess the required content knowledge of English, knowledge, and skills of using appropriate teaching methodology and the skills of using information and communication technology (ICT) of the potential teachers to teach English for grade 9 to 12. Such teachers are expected to have certain competencies. The content of this curriculum is based on the Teacher Competency Framework, 2072 and the curriculum of minimum academic and professional qualification required for this level. This curriculum is divided into two sections: (A) content knowledge and (B) pedagogical content knowledge and skills. It carries a total of 65 marks.
Objective
The overall objective of this curriculum is to test whether the teacher candidates meet the minimum requirement and possess the competencies needed to become an English teacher for grade 9 to 12 so that selection of a qualified and competent teacher can be ensured.
Section A: Content Knowledge 40 marks
- Theoretical Concepts of Language Learning
1.1. The changing world of English
1.1.1. English as a global language
1.1.2. English as a lingua franca
1.1.3. Native speaker varieties and other Englishes
1.1.4. Paradigm shifts in English language teaching
1.2. Theories of language learning
1.2.1. Empiricism vs. rationalism
1.2.2. Behaviourism vs. mentalism
1.2.3. Structuralism vs. generativism
1.3. Implications of the theories of language learning to language teaching
1.4. First language acquisition and second language learning
1.5. Factors affecting second language learning
1.6. Aspects of language teaching
1.7. Stages of language development in children
1.8. Krashen's theory of second language acquisition
2. Language and Linguistics
2.1. Definition of language
2.2. Characteristics of language
2.3. Levels of language
2.4. Varieties of language
2.5. English vowel and consonant system
2.6. Comparison between Nepali and English sound system
2.7. Grammatical units
2.8. Grammatical categories
2.9. Grammatical functions
2.10. Grammatical transformations
2.11. Error analysis and its implications
2.12 Pedagogical implication of linguistics
- Language Functions
3.1. Definition of communicative function and exponents
3.2. Grammatical function vs. communicative function
3.3. Form function relationship
3.4. Language functions included in secondary level English curriculum (with their exponents)
3.5. Communicative competence (concept and models)
3.6. Classification of language functions
3.6.1. Socializing
3.6.2. Making a query
3.6.3. Getting things done
3.6.4. Expressing moral and emotional attitudes
3.6.5. Expressing intellectual attitudes
3.6.6. Expressing modal attitudes
3.6.7. Importing factual information
4. Literature for Language Development
4.1. Definition of literature
4.2. Basic qualities of literature
4.3. Classification of literary gem-es
4.4. Literary universals
4.5. The language of literature
4.6. Figures of speech
4.7. Prosodic features
4.8. Approaches to using literature with language learners
4.9. Aims and objectives of using literature
4.10. Value of literature to language teaching
5. English Language Teacher's Professional Development
5.1. Profession and professionalism
5.2. Teacher training vs. teacher development
5.3. Importance of professional development
5.4. Strategies for English language teacher's professional development
5.4.1. Action research
5.4.2. Workshops, conferences, and seminars
5.4.3. Self-monitoring and mentoring
5.4.4. Keeping a teaching journal
5.4.5. Peer coaching
5.4.6. Portfolios
5.4.7. Analyzing critical incidents
5.4.8. Using open and distance learning modes
5.5. Main goals of professional development of English teachers
5.6. Stages of a teacher's professional life cycle
5.7. Teacher professional development programs, policies, and practices in Nepal
5.8. Problems of professional development of English teachers
6. English Language Teaching in Nepal
6.1. Situation analysis
6.2. Issues and challenges
6.3. Solutions
7. English Language Teaching Aids and Resources
7. 1. Introduction
7.2. Importance
7.3. Types
7.4. Low cost and no cost teaching materials
7.5. ELT games, songs and problem solving activities
8. Reading and Writing in English
8.1. Reading prose and poetry
8.2. Reading sub-skills and strategies
8.2.1. Identifying explicitly stated information
8.2.2. Identifying implicit information
8.2.3. Skimming
8.2.4. Scanning
8.2.5. Making inferences
8.2.6. Getting meaning of words from contexts
8.2.7. Identifying main ideas and supporting details
8.2.8. Giving title to the text
8.2.9. Identifying purpose and attitude of the author
8.3. Writing different types of texts
8.3.1. Curriculum vitae (CV)/Resume
8.3.2. Essays (argumentative, descriptive, and narrative)
8.3.3. Book reviews
8.3.4. News stories
8.3.5. Job application
8.3.6. Personal letter
Section B: Pedagogical Content Knowledge and Skills 25 marks
9. Secondary Level English Curriculum Textbook and Teacher's Guide
9.1. Secondary Level English Curriculum
9.1.1. Concept of curriculum
9.1.2.Characteristics of an ELT curriculum
9.1.3. Elements of an ELT curriculum
9.1.4. The Ideology of the curriculum
9.1.5. Steps and procedures of curriculum development
9.1.6. School level curriculum development process in Nepal
9.1.7. Present secondary English curriculum (introduction, structure, features)
9.1.8. Competency-based curriculum
9.1.9. Critical analysis of the present secondary level English curriculum
9.1.10. Test specification grid (concept, importance, use)
9.2 Secondary Level English Textbooks
10.2.1. Introduction to textbook
10.2.2. Types of textbooks: traditional vs. communicative
10.2.3. Advantages and limitations of using the textbook
10.2.4. Parameters of textbook analysis
10.2.5. Analysis of present secondary level textbooks
10.2.6. Characteristics of present secondary level textbooks
10.2.7. Strengths and weaknesses of present secondary level textbooks
10.2.8. Adapting textbooks
10.2.9. Teaching without textbooks
9.3. Teacher's Guide
10.3.1. Introduction
10.3.2. Elements of a teacher's guide
10.3.3. Use and importance of a teacher's guide
10.3.4. Present status of using the teacher's guide
10.3.5. Creative use of the teacher's guide
10. English Language Teaching Approaches, Methods and Techniques
10.1. Approaches and methods of English language teaching (principal features, classroom procedure, teacher and learner roles, assessment)
10.1.1. Grammar translation method
10.1.2. Direct method
10.1.3. Audio-lingual method
10.1.4. Oral structural and situational (OSS) approach
10.1.5. Communicative approach
10.1.6. Community language learning
10.1.7. Content-based instruction
10.1.8. Multiple intelligences
10.1.9. Task-based approach
10.1.10. A principled approach
10.1.11. Post method pedagogy
10.2. Techniques of English language teaching
10.2.1. Teacher-centered vs. learner centered techniques
10.2.2. Learner-centered techniques (Project work, Pair work, Group work, Strip story, Drama,
10.2.3. Simulation and role play, Quick write, Mind map, Brainstorming)
10.2.4. Teacher centered techniques (Lecture, Explanation, Illustration, Demonstration, Drill)
11. Teaching Language Skills
11.1. Teaching Listening
11.1.2.Features of real life listening situations
11.1.3. Factors that make listening difficult
11.1.4. Intensive and extensive listening
11.1.5. Principles of teaching listening
11.1.6. Listening sub-skills
11.1.7. Stages of teaching listening
11.1.8. Techniques and activities for teaching listening
11.2. Teaching Speaking
11.2.1. Components of speaking: pronunciation, stress, intonation
11.2.3. Features of a successful speaking activity
11.2.3. Problems of speaking activities and the ways to address them
11.2.4. Developing discussion skills in ELT classroom
11.2.5. Fluency vs. accuracy
11.2.6. Stages of teaching speaking
11.2.7. Communicative activities for teaching speaking
11.3. Teaching Reading
11.3.1. Nature of reading
11.3.2. Stages of reading development
11.3.3. Reading sub-skills
11.3.4. Intensive vs. extensive reading
11.3.5. Features of efficient reading
11.3.5. Principles of teaching reading
11.3.6. Types of reading
11.3.7. Approaches to reading
11.3.8. Stages of teaching reading
11.3.9. Techniques and activities for teaching reading
11.4. Teaching Writing
11.4.1.Spoken vs. written discourse
11.4.2. Components of writing
11.4.3. Stages of development in writing
11.4.5. Approaches to teaching writing: process vs. product
11.4.6. Techniques and activities for teaching writing
11.4.7. Teaching students to self edit
12. Teaching Language Aspects
12.1. Teaching Vocabulary
12.1.1. Aspects of learning a word: from, meaning, grammar, use
12.1.2. Criteria for selecting vocabulary
12.1.3. Active vs. passive vocabulary
12.1.4. Games and activities for vocabulary development
12.1.5. Activities of teaching the meaning of words
12.1.6. Activities for teaching the pronunciation of words
12.1.7. Activities for teaching the spelling words
12.2. Teaching Language Functions
12.2.1. Stages of teaching language functions
12.2.2. Activities for teaching language functions
12.3. Teaching Grammar
12.3.1. Arguments for and against teaching grammar
12.3.2. Place of grammar under different methods
12.3.3. Basic principles for teaching grammar (the criteria of efficiency and appropriacy)
12.3.4. Approaches to teaching grammar (deductive, inductive and text-based: concept, procedure, sample lesson plans, assessment)
12.3.5. Consciousness raising in grammar teaching (Richards 167)
12.3.6. Presenting and explaining grammar
12.3.7. Games and communicative activities for teaching grammar
12.3.8. Responding to grammatical errors
12.4. Teaching Pronunciation
12.4.1. Importance of teaching pronunciation
12.4.2. Problems in teaching pronunciation
12.4.3. Issues related to teaching pronunciation
12.4.4. Techniques and activities for teaching pronunciation
13. Teaching Literature
13.1. Teaching poetry
13.2. Teaching short story
13.3. Teaching essay
13.4. Teaching drama
14. English Language Testing
14.1. Concept of testing
14.2. Reasons for testing
14.3. Relationship between teaching and testing 14.4. Qualities of a good test
14.5. Classification of language tests
14.6. Testing language skills
14.7. Testing language aspects
14.8. Designing test tasks for testing language skills and aspects
15. Instructional Planning
15.1. Introduction to instructional planning
15.2. Importance of instructional planning
15.3. Types of instructional plan
15.4. Construction and use of academic calendar, annual plan, term plan, unit plan and daily lesson plan
15.5. Value of lesson planning
15.6. Essential elements of a lesson plan
15.7. Characteristics of a good lesson plan
15.8. Lesson sequences (PPP model, task-based model and ESA model)
16. Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in English Language Teaching
16.1. Importance of ICT in English language teaching
16.2. Key challenges in integrating ICTs in English language teaching
16.3. Use of ICT tools (such as multimedia, mobile phones, computers, the Internet, etc.) in English language teaching
16.4. Computer-based presentation technology (interactive whiteboard, multimedia projector)
16.5. Electronic dictionaries, CD-ROMS and online dictionaries
16.6. Power Point Presentation
16.7. Searching materials in the Internet
16.8. Virtual learning
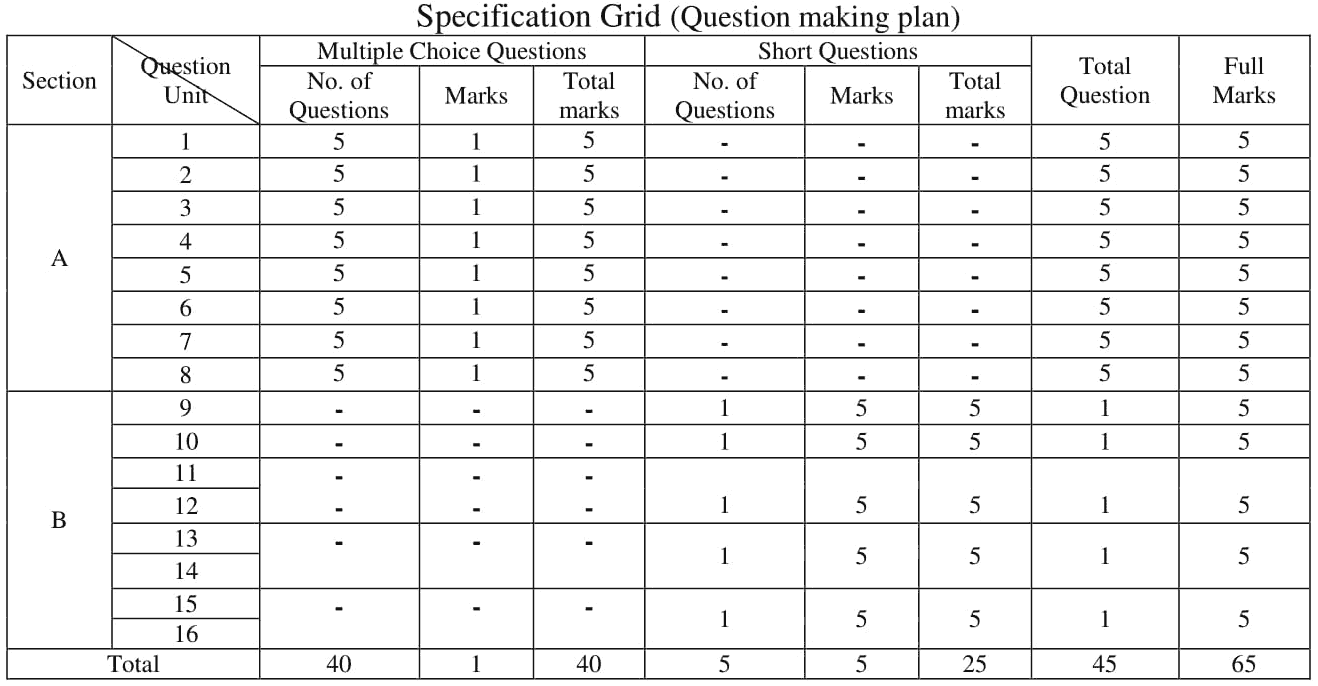
Specification Grid (Question making plan)
|
Section |
stion Uni |
Multiple Choice Questions |
Shoit Questions |
Total |
Full |
||||
|
No. of |
Marks |
Total |
No. of |
Marks |
Total |
||||
|
A |
1 |
5 |
1 |
5 |
|
- |
- |
5 |
5 |
|
2 |
5 |
1 |
5 |
- |
- |
- |
5 |
5 |
|
|
3 |
5 |
1 |
5 |
- |
- |
- |
5 |
5 |
|
|
4 |
5 |
1 |
5 |
- |
- |
- |
5 |
5 |
|
|
5 |
5 |
1 |
5 |
- |
_ |
- |
5 |
5 |
|
|
6 |
5 |
1 |
5 |
- |
|
- |
5 |
5 |
|
|
7 |
5 |
1 |
5 |
- |
_ |
- |
5 |
5 |
|
|
8 |
5 |
1 |
5 |
- |
- |
- |
5 |
5 |
|
|
B |
9 |
- |
_ |
_ |
1 |
5 |
5 |
1 |
5 |
|
10 |
- |
- |
- |
I |
5 |
5 |
1 |
5 |
|
|
11 |
- |
- |
- |
1 |
5 |
5 |
1 |
5 |
|
|
12 |
|||||||||
|
13 |
- |
- |
|
1 |
5 |
5 |
1 |
5 |
|
|
14 |
|||||||||
|
15 |
- |
- |
- |
1 |
5 |
5 |
1 |
5 |
|
|
16 |
|||||||||
|
Total |
40 |
1 |
40 |
5 |
5 |
25 |
45 |
65 |
|
Note:
- Total 3 hours the time is allocated for testing: forty-five minutes for objective questions and two hours and fifteen minutes for subjective questions.
- The objective and subjective tests will be conducted in the same setting, and the subjective test will begin as soon as the objective test is completed.
- The questions will be asked covering all the levels of the cognitive domain.
- The short questions will focus on knowledge, skills, and application, and the long questions will focus on creativity and the pragmatic aspects related to teaching.
- The priority will be given to those answers which are creative and based on the critical analysis of the practical aspects of learning
Please Download Collegenp App from Playstore: Install Now for regular Update