Government of Nepal, Teachers Service Commission
Secondary Level Curriculum of Subjective Examination- 2076
Subject: Computer Science
Full Marks: 100
Time: 3 Hours
Section: A
Unit 1. Computer Fundamentals, Number System and Digital Logic
1.1 Fundamentals of computer
1.2 Computer Hardware: An input device, an Output device, Hardware interface, Storage devices
1.3 Computer Architecture, Central processing unit, Control unit, Computer arithmetic, input-output organization, memory organization
1.4 Number system, Binary Arithmetic, Base Conversion
1.5 Boolean Logic and Boolean algebra
1.6 Introduction to the digital system, Logic gates and Boolean algebra, Boolean function
1.7 Concept of Sequential and Combinational Circuits
1.8 Concept of Microprocessor
Unit 2. Computer Application, Multimedia, and Graphics
2.1 Computer software and its classification
2.2 Office Automation application: Word processor, Spread Sheet, and Presentation
2.3 Database packages and its applications
2.4 Concept Multimedia, Component of Multimedia: Text, Graphics, Audio, Video, and Animation
2.5 Application of Multimedia, Computer Graphics (image size, format, and editing)
2.6Use of Computer Application and Multimedia in teaching and learning
Unit 3. Programming Concepts and Object-Oriented Programming
3.1 Programming Language Translators, Pseudocode, Algorithm and Flow chart
3.2 Programming in QBasic, Opening, reading and writing data file, modular programming approach, function and Sub procedure
3.3 Programming Language types and generations
3.4 C-Programming: Keywords, identifier's, data types, constants and variables, input, output and control statement, functions, array, pointer, structure and file handling concept
3.5Object Oriented Programming (OOP): Class, Object, Encapsulation, Polymorphism and Inheritance, Object-Oriented Programming with C++ and Java Programming
Unit 4. Web Technology
4.1 Concept of Internet and Email
4.2 Internet technology: WWW, Social Media and Web 2.0, Tire architecture, HTTP
4.3 HTML Tag and web site design concept
4.4 CSS (Inline, embedded and external) and JavaScript
4.5 Concept of PHP and MySQL
4.6Content Management System (CMS) and Practices
Unit 5. Computer Network and Data Communication
5.1 Concept of Telecommunication and Computer Networking
5.2 Data communication and communication System
5.3 Elements of Data Communication/Transmission, Simplex, Half duplex, and Full-duplex communication mode
5.4 Concept of LAN and WAN, Transmission Medium: Guided and Unguided, Elements of Network
5.5 Types of Network, Network Architecture, Topologies, Protocols
5.6 OSI reference model and TCP/IP model
5.7 Network Security, Conventional Encryption, Cryptography, Authentication and Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)VPN
Section: B
Unit 6. Data Structure, Algorithm and Database Management System
6.1 Introduction to Data Structure and Algorithm
6.2 Stacks, Queues and Lists, Sorting and Searching algorithms, Tree, and Graph
6.3 Concept of Database model: Relational Model, Entity-Relationship Data Model
6.4 DDL, DDL and DCL, Relational Algebra, Structured Query Language (SQL) and Integrity constraints
6.5 Database Normalization (1NF, 2NF, 3NF, and BCNF)
6.6 Concurrency Control and Transaction Processing
6.7 Database security and recovery
6.8 Concept of Distributed Database, NoSQL, Bigdata, Data warehouse, and data mining
Unit 7. Operating System
7.1 Introduction of Operating System,
7.2 Window operating system and Basic Operation
7.3 Open source operating system and mobile operating system,
7.4 Process management,
7.5 Memory management,
7.6 Storage management,
7.7 System administration using Linux
Unit 8. Software Development and Software Project Management
8.1 Fundamentals of System Analysis and System Design,
8.2 Feasibility Analysis,
8.3 Software process and software development model
8.4 Requirement Engineering and Software Architecture
8.5 Software Testing, Verification, and Validation
8.6 Software Re-engineering
8.7 Software Project Management: initiation, planning, execution, and closing
Unit 9. Recent Technology, Ethical and Social Issue
9.1 Concept of Cloud Computing: SaSS, PaSS, IaSS
9.2 Concept of Artificial Intelligence: Virtual Reality, IoT, Augmented Reality
9.3 e-Enable Services: E-Governance, e-commerce, e-medicine
9.4 Ethical and Social Issues in ICT: Security threats, Malicious software and Spam, malicious codes, security and ethical challenge, Digital Citizenship, Digital Footprint, Opportunities and threats in Social Media, Digital society and computer ethics, Cybercrime,
9.5 Authentication systems: Password, biometric, Firewalls, Antivirus software,
9.6 Backup System, Hardware Security, Power protection device (Volt guard, Spike guard, UPS)
9.7 Intellectual Property Right, Concept of Digital Signature, Cyberlaw in Nepal
Unit 10. ICT in Education
10.1 ICT Education and ICT in Education
10.2 Learning theory and practices: Constructivism, Connectivism, Network, PBL
10.3 E-learning and ICT Education pedagogy: e-learning Concept and Characteristics, ICT integrated lessons, ICT in Assessment,
10.4 e-Learning 3.0 and ICT educational tools
10.5 Learning Management System: MOODLE based learning Management system
10.6 ICT for Teacher Professional Development, Teachers ICT competencies
10.7 ICT in Education in ICT policy in Nepal and Digital Nepal Framework
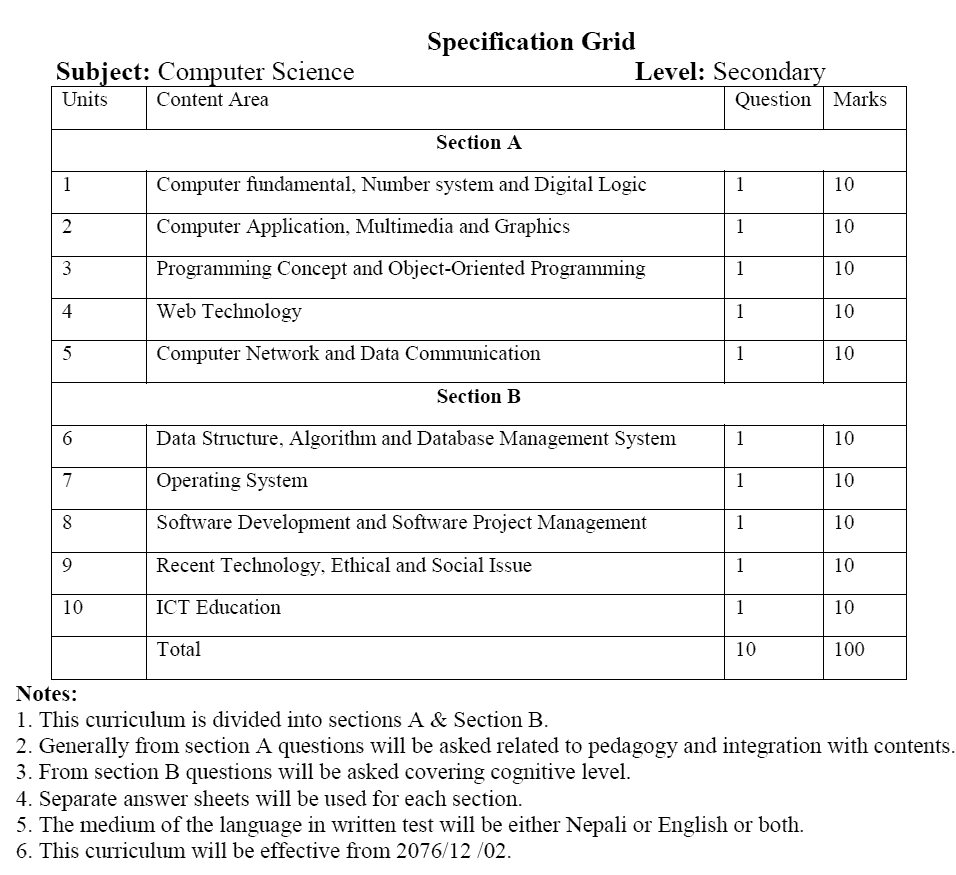
Specification Grid:
Subject: Computer Science Level: Secondary
|
Content Area |
Question |
Marks |
|
Section A |
|
|
|
Unit - 1: Computer fundamental, Number system and Digital Logic |
1 |
10 |
|
Unit - 2: Computer Application, Multimedia and Graphics |
1 |
10 |
|
Unit - 3: Programming Concept and Object-Oriented Programming |
1 |
10 |
|
Unit - 4: Web Technology |
1 |
10 |
|
Unit - 5: Computer Network and Data Communication |
1 |
10 |
|
Section B |
|
|
|
Unit - 6: Data Structure, Algorithm and Database Management System |
1 |
10 |
|
Unit - 7: Operating System |
1 |
10 |
|
Unit - 8: Software Development and Software Project Management |
1 |
10 |
|
Unit - 9: Recent Technology, Ethical and Social Issue |
1 |
10 |
|
Unit - 10: ICT Education |
1 |
10 |
|
Total |
10 |
100 |
Notes:
- This curriculum is divided into sections A & Section B.
- Generally from the section, questions will be asked related to pedagogy and integration with contents.
- From section, B questions will be asked covering the cognitive level.
- Separate answer sheets will be used for each section.
- The medium of the language in the written test will be either Nepali or English or both.
- This curriculum will be effective from 2076/12 /02.
Model Question
Computer Science
Secondary Level (Grade 9-12)
Group A (10 x 5=50)
Attempt All questions:
- a) What are the components of a computer system? How do you describe it in the classroom?
- Describe the logic gates demonstration techniques for teaching.
- What are the major features of a word processor? How do you implement these features in classroom teaching-learning purposes? Explain with examples.
- a) Describe the array. Explain the methods to a practical demonstration of the array in laboratory work.
- Explain the inheritance concept in C++/Java programming language to classroom teaching.
- Demonstrate the different types of CSS and how do you show to integration in an HTML page on teaching.
- How do you teach the OSI reference model in higher-order thinking? Describe.
Group B (10 x 5=50) Attempt All questions
- Describe the software development process. How do apply the verification and validation process in software quality assurance?
- Describe the different categories of cybercrime and countermeasure methods to prevention form cybercrime.
- Explain the ICT integrated pedagogy and e-learning tools to the classroom teaching.
- Demonstrate the quick sort algorithm with an example.
- Describe the round-robin CPU scheduling algorithm with an example.