Unraveling the Mysteries of the Human Brain
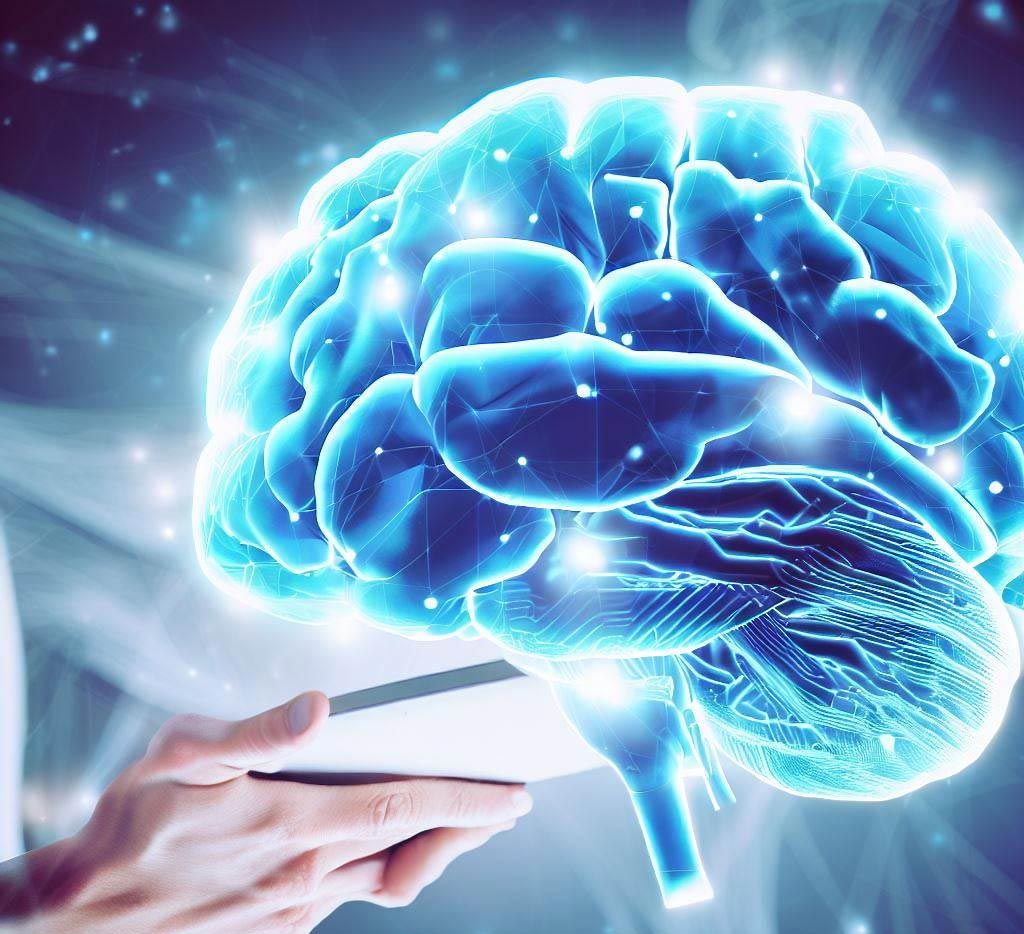
The human brain is the command center for the human nervous system, acting as an intricate organ responsible for our thoughts, feelings, memories, and so much more. As you journey through this comprehensive exploration of the brain's complex anatomy, its stunning capabilities, and the factors influencing its health, we hope to spark a deeper appreciation and understanding of your brain's magnificent intricacies.
The Anatomy of the Brain and its Main Regions
The human brain is broadly divided into three parts: the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the brainstem.
-
The Cerebrum: This is the largest part of the brain, housing higher brain functions such as thinking, learning, and consciousness. It is divided into two hemispheres and further split into four main regions or 'lobes': the frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal lobes.
-
The Cerebellum: Positioned below the cerebrum, the cerebellum is responsible for motor control, balance, and coordination.
-
The Brainstem: This part of the brain connects the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord, facilitating the transfer of messages. It controls many basic functions such as heart rate, breathing, and sleep.
Understanding Human Brain Functions: Roles of Different Brain Regions
Each region of the brain plays a critical role in our daily life and cognition.
-
Frontal Lobe: Associated with reasoning, motor skills, higher level cognition, and expressive language. Damage to the frontal lobe can lead to changes in sexual habits, socialization, and attention as well as increased risk-taking.
-
Temporal Lobe: Associated with interpreting sounds and language we hear, as well as memory formation.
-
Parietal Lobe: The parietal lobe processes tactile sensory information such as pressure, touch, and pain.
-
Occipital Lobe: The occipital lobe is associated with interpreting visual stimuli and information.
-
Cerebellum: As the 'little brain', it controls essential functions related to motor skills, such as coordination, precision, and accurate timing.
-
Brainstem: It controls numerous basic bodily functions and reflexes, like heart rate, breathing, and swallowing.
The Wonder of Brain Cells: Neurons and Communication
Neurons, or nerve cells, are the building blocks of the nervous system. They transmit signals, or 'messages,' throughout the body, allowing us to respond to stimuli and carry out actions. This process is facilitated by neurotransmitters, chemical messengers that transmit signals across a synapse, the small gap between neurons.
In the words of Santiago Ramón y Cajal, a Nobel laureate often considered the father of modern neuroscience, "The neuron doctrine, the fundamental organizational and functional principle of the nervous system, states that the neuron is the elementary functional unit of the nervous system and that neurons communicate with each other by contact, not continuity." This doctrine underpins our understanding of how the brain processes and interprets information.
How Does the Brain Process Information?
The brain processes information through the simultaneous firing of billions of neurons. These neural circuits, or 'pathways', form the basis of everything we think, do, and experience. A simple analogy might be to consider the brain as a computer, with neurons as the circuits that make everything run smoothly.
The Impact of Lifestyle on Brain Health
Our lifestyles, encompassing our diet, sleep, exercise, and mental health, play a significant role in our brain health and cognitive function.
-
Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, healthy fats, and whole grains can support brain health. Certain nutrients, like omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins, and antioxidants, are particularly beneficial.
-
Sleep: Quality sleep is essential for the consolidation of memory and learning, emotional regulation, and overall brain health.
-
Exercise: Regular physical activity increases blood flow to the brain, reduces inflammation, and stimulates the growth of new neurons.
-
Mental Health: Chronic stress, anxiety, and depression can have a detrimental impact on the brain, impairing cognition, memory, and mood.
The Brain Development Stages Throughout Life
The human brain undergoes significant changes throughout life. It begins to form just three weeks after conception, rapidly growing and developing during pregnancy. Childhood and adolescence are periods of rapid brain growth and change, with ongoing development into our mid-20s. Even in adulthood, the brain retains the ability to change and adapt—a phenomenon known as neuroplasticity.
Neuroplasticity in the Human Brain
Neuroplasticity, or brain plasticity, refers to the brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life. Neuroplasticity allows the neurons (nerve cells) in the brain to compensate for injury and disease and to adjust their activities in response to new situations or to changes in their environment.
Dr. Norman Doidge, a renowned psychiatrist and author of 'The Brain That Changes Itself', encapsulates the concept beautifully, stating that "The brain is not, as was thought, like an inanimate machine, hardwired or like a computer. But rather, it's a plastic, living organ that can actually change its own structure and function, even into old age."
The Role of Memory and Cognition in the Brain's Functioning
Memory and cognition are vital elements of our brain's functionality. Cognition refers to a range of high-level brain functions including the ability to learn and remember information, organize, plan and problem-solve, focus, maintain, and shift attention, understand and use language, visually perceive the environment, and accurately interpret the emotions of others. Memory, a component of cognition, is the process of storing and recalling information. These cognitive processes play a significant role in all our daily activities and interactions.
The Effects of Mental Health on Brain Functionality
Mental health is deeply intertwined with brain health. Mental illnesses, such as depression and anxiety, can alter the structure and function of various brain regions, impacting memory, attention, cognitive abilities, and emotional regulation. Therefore, caring for our mental health is an integral aspect of overall brain health.
This exploration of the inner workings of the human brain is not only a testament to the incredible complexity and adaptability of this organ but also a call to action. Understanding the importance of brain health and the factors that influence it empowers us to make lifestyle choices that support our well-being and cognitive longevity. Our brain, with its amazing capabilities and intricate structure, undoubtedly deserves this commitment to its care and understanding.
Conclusion
The human brain is a remarkable organ, a testimony to the incredible capabilities of evolution and biology. Its intricate structure and vast functionality govern everything we are and do. Despite decades of research, we're still just scratching the surface of understanding this phenomenal organ. As we continue to explore the mysteries of the brain, one thing is clear—caring for our brain health is of paramount importance. By adopting a brain-friendly lifestyle and seeking to understand the inner workings of our brain, we can optimize its function and enrich our lives in countless ways.
Remember, as Bernard Katz, a Nobel laureate in Physiology, wisely said, "Each of us is a unique individual, but we share one very powerful attribute – the ability to create our own mental and emotional health through our actions." Let's strive to take the right actions towards maintaining and enhancing the health of our invaluable brain.
Mental Health