Overview
The Nepal Medical Council (NMC) is a pivotal institution in Nepal's healthcare sector. Established in 1964, it plays a crucial role in regulating and enhancing medical practice and education in Nepal. In this guide, we'll explore the history, structure, and functions of the NMC, shedding light on its impact on healthcare standards and practices in Nepal.

Objectives of the Nepal Medical Council (NMC)
-
Regulate Medical Professionals: To maintain a comprehensive registry of qualified doctors in Nepal, including medical and dental practitioners.
-
Ensure Quality Education: To oversee and enhance the quality of medical education in Nepal, ensuring that it meets national and international standards.
-
Conduct Licensing Examinations: To administer and manage licensing examinations for medical graduates, ensuring their readiness and competence for professional practice.
-
Monitor Healthcare Services: To regularly assess and monitor the quality of healthcare services provided in Nepal, aiming for continual improvement.
-
Establish Ethical Standards: To set, promote, and enforce ethical standards in medical practice, ensuring that healthcare professionals adhere to the highest moral principles.
-
Standardize Medical Practices: To develop and implement standardized protocols and guidelines for medical practice across the country.
-
Enforce Disciplinary Measures: To take appropriate disciplinary actions against medical professionals who breach ethical or professional standards.
-
Promote Continuous Professional Development: To encourage and facilitate ongoing learning and professional development among registered medical practitioners.
-
Enhance Public Health Safety: To work towards safeguarding public health by ensuring competent and ethical medical practice throughout Nepal.
-
Facilitate International Collaboration: To collaborate with international medical bodies and institutions, enhancing the global integration and recognition of Nepal's medical community.
-
Advocate for Health Policy Reforms: To advise and assist the government in the formulation and implementation of health policies and reforms.
-
Address Public Concerns and Complaints: To provide a platform for addressing public grievances related to medical practices and healthcare services.
Historical Background
-
Establishment: The NMC was established in 1964, following the first National Conference of the Nepal Medical Association in 1963.
-
Legal Framework: The council began operations under the NMC Act, with its rules and regulations coming into effect gradually from 1965 to 1977.
-
Amendments: The NMC Act has undergone several amendments to refine its structure and functions, the latest of which was in 2001.
Roles and Responsibilities
-
Registration and Licensing: A key function of the NMC is to register qualified doctors and conduct licensing examinations.
-
Monitoring and Regulation: The NMC oversees medical education in Nepal, ensuring quality and adherence to standards.
-
Ethical Practice Enforcement: It establishes and enforces ethical standards and practices in healthcare.
Structure of the NMC
-
Composition: The NMC comprises 19 members, including a Chairman, a Vice-Chairman, and 17 other members from diverse backgrounds.
-
Term of Service: Members serve for a four-year term.
-
Registrar: A government-nominated Registrar oversees the execution of NMC decisions.
Impact on Healthcare in Nepal
-
Quality Control: The NMC plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality of medical education and healthcare services.
-
Standardization: It aims to standardize medical practices nationwide.
-
Disciplinary Actions: The council takes action against breaches of ethical and professional standards in healthcare.
Key Functions of the NMC
-
Quality Control in Medical Education: Ensuring the standard and integrity of medical education in Nepal.
-
Health Services Oversight: Monitoring and enhancing the quality of health services in the country.
-
Ethical Healthcare Practices: Establishing and promoting ethical standards in healthcare.
-
Medical Practice Standardization: Setting and maintaining standards in medical practices.
-
Disciplinary Actions: Addressing breaches of ethical or standard healthcare practices.
Current Structure and Composition
-
Chairman: Nominated by the Government of Nepal, with at least 20 years of experience as a registered doctor.
-
Vice-Chairman: An elected registered medical doctor with a minimum of 15 years of experience.
-
Members: Includes representatives from various medical and dental associations, government nominees, and elected registered doctors.
-
Registrar: Appointed by the Government of Nepal to implement the decisions and activities of the NMC.
Statistics and Current Status
Registered Doctors: As of January 2024, the NMC registered 45,498 doctors. This includes 30,027 medical doctors and 4,883 dentists. Additionally, there are 34,910 doctors and 10,588 specialists registered to practice in Nepal, according to the Nepal Medical Council (NMC).
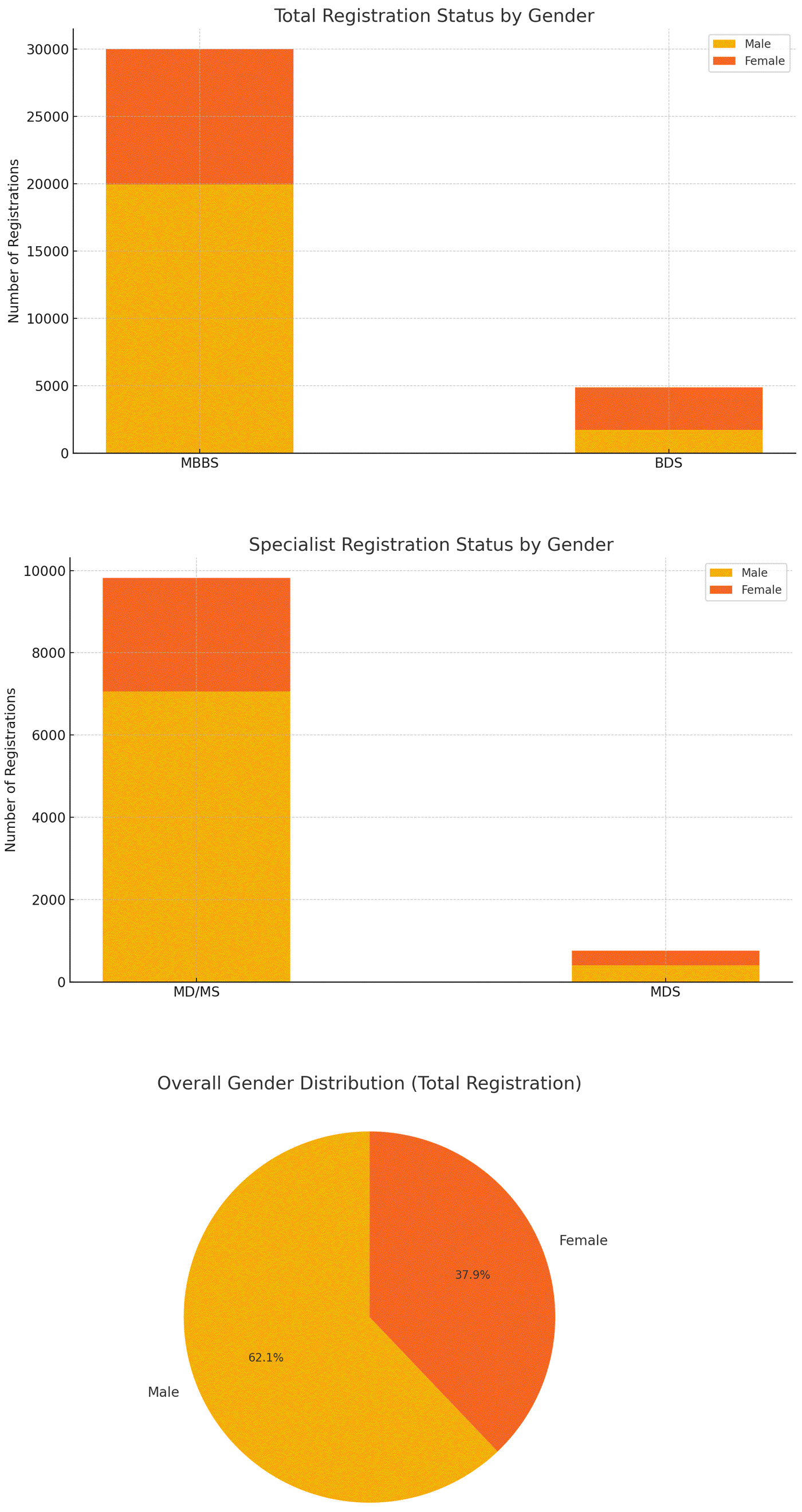
Total Registration Status
-
MBBS
-
Male: 19,954
-
Female: 10,073
-
Total: 30,027
-
-
BDS
-
Male: 1,727
-
Female: 3,156
-
Total: 4,883
-
-
Grand Total
-
Male: 21,681
-
Female: 13,229
-
Total: 34,910
-
Specialist Registration Status
-
MD/MS
-
Male: 7,063
-
Female: 2,760
-
Total: 9,823
-
-
MDS
-
Male: 404
-
Female: 361
-
Total: 765
-
-
Grand Total
-
Male: 7,467
-
Female: 3,121
-
Total: 10,588
-
(Medical Registration Statistics (As of December 31, 2023)
Contact Details:
-
Address: Bansbari, Kathmandu, Post Box No. 13890
-
Phone Numbers: 01-4377164 / 01-4371954
-
Email: registration@nmc.org.np (Registration propose only); goodstanding@nmc.org.np (Goodstanding propose only); verification@nmc.org.np and retotaling@nmc.org.np
-
Website: www.nmc.org.np










