
Bachelor of Computer Application (BCA) – Tribhuvan University (TU): Syllabus, Entrance, Skills, Careers
BCA TU is a four-year program that helps students move from basic coding to applied software practice with projects and an internship.
The course sits under Tribhuvan University’s Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences (FOHSS) and runs in English across eight semesters. The official syllabus sets a minimum of 126 credits, structured to build programming skill, systems knowledge, and professional readiness.
Table of Content
- Bachelor of Computer Application (BCA) – Tribhuvan University (TU): Syllabus, Entrance, Skills, Careers
- Who This Guide Helps
- Program Snapshot
- Why Choose BCA TU
- TU BCA Syllabus: How the 8 Semesters Flow
- Credits, Assessment, and Attendance
- Entrance Pattern and Weightage
- Entrance preparation that works
- Simple 8-Week Entrance Plan
- Who Thrives in BCA TU
- What You Can Do After BCA TU
- Project work and internship: how learning turns into a portfolio
- Skills you build
- How to shortlist a campus
- Study Routines That Work
- Projects That Signal Readiness
- Internship: From Classroom to Work
- Further Study After BCA
- BCA TU vs. BSc CSIT vs. BIT
- Ethics, Law, and Safe Practice
- On-Campus Learning Tips
- Admissions Steps
- Real Student Example
- How to Build a Portfolio Semester by Semester
- Further Study and TNE Context
- Final Thought
- FAQs
Who This Guide Helps
Students weighing the Tribhuvan University BCA option. Parents who want clear facts. Counselors who need a quick reference during admissions. Career switchers planning a return to study. The tone stays neutral and practical.
Program Snapshot
-
Awarding Body: Tribhuvan University, FOHSS.
-
Length: 4 years, 8 semesters, 126 credits.
-
Medium: English.
-
Core Focus: Programming, software design, databases, operating systems, networks, web/mobile development, projects, and internship.
Why Choose BCA TU
Reach and continuity. TU has a large national footprint. Public sources on higher-education EMIS describe TU’s role across programs and campuses, which supports access and networks for students across Nepal.
Practical outcomes. The BCA syllabus blends coding, systems, and business awareness. Final-year projects and an internship add workplace context and help students build a portfolio that hiring teams can read in minutes.
Wider exposure. A transnational education (TNE) study outlines growth and interest for Nepal, adding pathways for remote collaboration and further study.
TU BCA Syllabus: How the 8 Semesters Flow
The official structure spreads learning across programming, systems, quantitative skills, management, social science, and applied courses. A plain-English view below mirrors what students report on campus pages and FOHSS information.
Year 1: Foundations
-
Computer Fundamentals & Digital Logic – how a computer works, number systems, gates, simple circuits.
-
Programming in C – syntax, control flow, functions, arrays, pointers, file handling.
-
Mathematics I–II – algebra, functions, sequences, basic calculus ideas for later courses.
-
English I–II – reading, composition, presentation.
-
Microprocessor & Architecture; Accounting; Society & Technology – basic hardware ideas, financial literacy, and a social lens on computing.
Year 2: From Code to Software
-
Data Structures & Algorithms – lists, stacks, queues, trees, graphs, sorting, searching.
-
Probability & Statistics; Numerical Methods – data literacy, approximation, error.
-
OOP in Java – classes, inheritance, interfaces, collections, exceptions.
-
Web Technologies – HTML/CSS/JS basics, simple full-stack tasks.
-
Operating Systems; DBMS – processes, memory, file systems; relational models, SQL.
-
Scripting – automation with a light scripting language.
-
Project I – a practical course with documentation and demo.
Year 3: Systems and Applications
-
Computer Networks – models, protocols, routing, basic socket ideas.
-
.NET Technologies; Advanced Java or similar – another productive stack for desktop/web.
-
Management Information Systems & e-Business – how software supports decisions and services.
-
Graphics/Animation; Mobile Programming; Distributed Systems – visual computing, mobile apps, networked services.
-
Applied Economics – market basics, cost thinking for projects.
Year 4: Practice, Ethics, and Transition to Work
-
Cloud Computing – fundamentals of hosted services and deployment models.
-
Cyber Law & Professional Ethics – policy and responsible practice.
-
Electives – focus areas from the department list.
-
Project III/Capstone & Internship – a final build and a supervised placement with logs, reviews, and a short presentation for assessment.
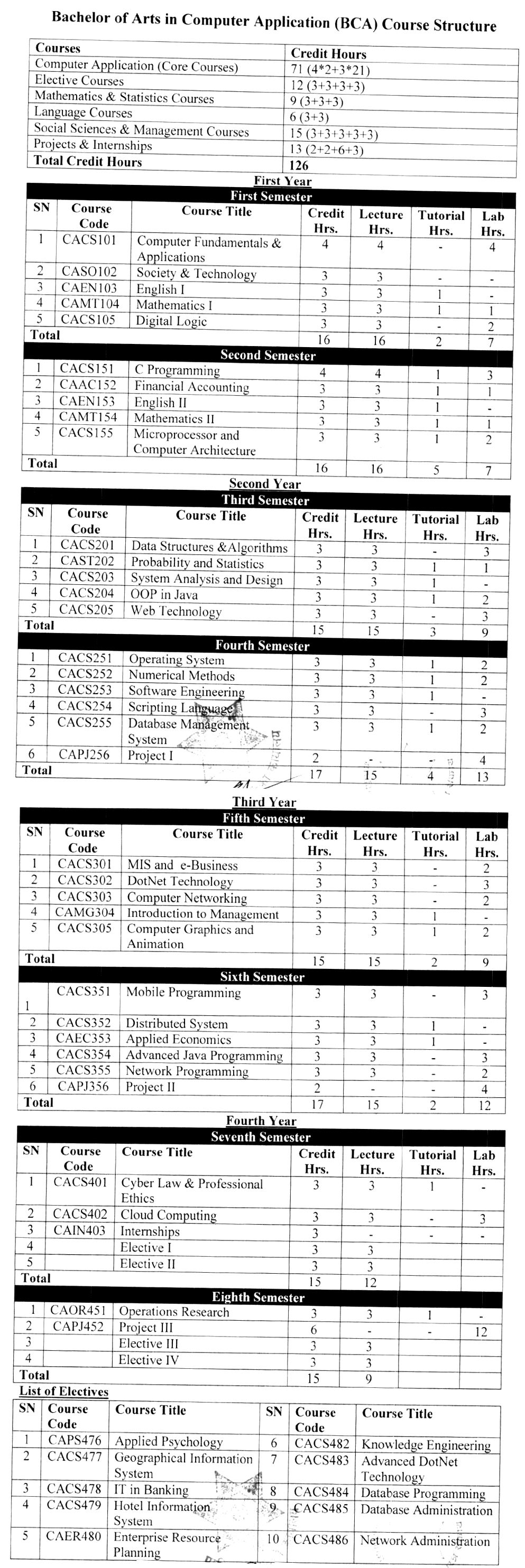
Credits, Assessment, and Attendance
The official syllabus fixes 126 credits over eight semesters. Course pages and handbooks describe mixed evaluation: internal work and a final exam, with practicals for lab-heavy courses. Check the latest FOHSS PDF each cycle for exact split and attendance rules.
Entrance Pattern and Weightage
The TU BCA entrance uses 100 objective questions. The common pattern published across FOHSS-linked sources and established education portals is:
-
Mathematics – 50%
-
English Grammar – 40%
-
General Knowledge – 10%
Application windows and admit cards run through the FOHSS registration system. Keep an eye on the official entrance portal for live notices.
Entrance preparation that works
Time split by weightage
-
Half your study hours for math, two-fifths for English, the rest for GK. That split mirrors the test.
Math
-
Algebra review, functions and graphs, sequences and series
-
Counting principles and basic probability
-
Speed drills with mixed sets to build accuracy under time pressure
English
-
Reading passages with a timer
-
Short grammar revisions with error-finding
-
One paragraph a day: define a topic, state a claim, support it with a short example
GK
-
Nepal geography and civics, common IT facts, national days and institutions
-
One page of notes per day, then a weekly self-quiz
Simple 8-Week Entrance Plan
Weeks 1–2: Algebra, functions, sequences, matrices basics. Grammar fundamentals: tense, agreement, modifiers. Read a short civic or science brief daily for GK.
Weeks 3–4: Trigonometry, permutations/combinations, probability. Sentence correction drills and cloze tests.
Weeks 5–6: Calculus ideas for rate and area. Set theory and basic logic. Reading comprehension under time.
Weeks 7–8: Two full mocks per week. Keep an error log. Review wrong answers before sleep. On test day, start with Math, move to English, finish with GK.
This sequence mirrors the Math 50 / English 40 / GK 10 split and trains speed without guesswork.
Who Thrives in BCA TU
-
Learners who code every day, even for 30 minutes.
-
Students who document work: short READMEs, comments, and a small reflection after each lab.
-
Group players who ask simple questions and accept feedback.
-
Anyone ready to connect math ideas with code and data.
-
Readers who can summarize an article in five lines, then relate it to a software task.
What You Can Do After BCA TU
Entry roles: Junior software developer, web developer, mobile developer, QA/automation associate, database associate, IT support.
Growth paths: Backend, cloud/DevOps, data/analytics with extra math, cybersecurity, business analysis/product.
Sectors: Services, fintech, health, education, telecom, NGOs. A TNE report adds remote and cross-border learning routes that complement local work.
What hiring teams scan first: a clean repo, small unit tests, clear commit messages, and one-page notes that explain trade-offs. Grades matter; proof of work speaks quicker.
Project work and internship: how learning turns into a portfolio
Project courses build from proposal and design to implementation and defense. The internship places you with a host organization under defined supervision and reporting. Defense panels usually include supervisor, coordinator/HOD, internal, and an external examiner. This structure trains you to plan, code, document, present, and respond to questions—core habits for the workplace.
Simple project roadmap
-
Problem framing: one user group, one pain point, one clear outcome
-
Version control from day one; short commits with meaningful messages
-
Readme with setup steps, feature list, and a short demo note
-
A brief reflection after each sprint: what worked, what broke, what to try next
Colleges and seats
There are about 4,500 seats for TU’s network. FoHSS posts yearly campus lists via notice PDFs. Use the latest list during counseling so your preferences match current approval.
Fees and budgeting
Public constituent campuses keep tuition lower. Private affiliated colleges post program totals on their sites. One published example from ICMS Samarpan shows a total of NPR 460,000 with a semester-wise split. Some directories mention totals near NPR 450,000 for BCA at private campuses in Kathmandu, though each college sets its own structure. Ask for the current official fee letter before you commit.
What to confirm with the accounts office
-
Admission fee, semester tuition, lab/library/exam fees
-
Installment plan, late fees, refundable deposits
-
Internship or project-related charges, if any
-
Scholarship rules and required documents
Skills you build
Technical
-
Programming in C and Java, with .NET and scripting exposure
-
Web development fundamentals and mobile development basics
-
SQL, database design, and admin concepts
-
Operating systems, computer networks, and distributed concepts
Human skills
-
Writing and presenting through English I–II and project defenses
-
Planning and teamwork through semester projects
-
Professional ethics and basic management exposure for client-facing roles
These outcomes align with FoHSS’s stated goals for BCA graduates: application users and developers who can contribute from day one.
How to shortlist a campus
-
Start from the latest FoHSS campus list in the notice section
-
Visit two or three colleges, speak with current students, and scan lab machines for the tools you will use
-
Ask for the official fee letter and a copy of the internship policy
-
Request samples of project reports from seniors and check the panel structure for defenses as per the curriculum
Study Routines That Work
Short daily reps beat all-night sessions. Many first-year learners report better recall with 25- to 40-minute coding blocks followed by a short summary in a notes file. A tidy GitHub repo becomes a study aid during finals and an easy share during internship interviews. That habit grows through Projects I–III and the final internship defense described in TU’s curriculum.
-
Weekly plan (about 25 focused hours): 12 coding, 5 reading and notes, 4 math/stats, 2 review, 2 portfolio curation.
-
Active recall: Turn each unit outcome into two or three short questions and quiz yourself.
-
Spaced practice: Repeat core problem sets across weeks instead of one long sprint.
-
Peer learning: Two friends; one topic each; rotate as mini-teachers.
-
Version control from week one: Even a short lab deserves commits, a README, and a tiny test.
Personal note: students I’ve coached kept a “10-minute log” after labs—what worked, what didn’t, what to try next time. The habit reduces repeat errors and lifts confidence during viva or demos.
Projects That Signal Readiness
Project I (semester IV) sits at the point where students can move from small lab tasks to a simple product. A good Project I has:
-
A clear problem line in three sentences.
-
One main feature and one nice-to-have.
-
A short test plan with two or three checks.
-
A README with screenshots and a setup note.
For Project II and III, add teamwork, a short sprint plan, and a user test with two peers outside your group. Keep every branch on Git. Your internship host will notice the habit.
Internship: From Classroom to Work
Final-semester internship connects course ideas with workplace routines. Keep weekly logs and a tiny demo video every other week. At the end:
-
One page on lessons learned.
-
A short clip where you explain one bug and how you fixed it.
-
A checklist that maps your internship tasks to syllabus units: OS concepts, DB triggers, REST calls, or test cases.
This small set helps during evaluation and future interviews. FOHSS sources and campus pages present the internship as supervised and assessed, which fits this approach.
Further Study After BCA
Many graduates move to MCA, MIT, MS (CS/IS) or MBA with a tech or product path. Add one or two industry certificates that match your stack:
-
Java (OCP) for those who love OOP.
-
AWS Cloud Practitioner/Associate for deployment basics.
-
Linux Essentials/LPIC-1 for systems grounding.
-
SQL certs for database roles.
-
CCNA for network interest.
-
ISTQB for QA/automation.
Pick one area and go deep over six months. One good case study beats several half-done badges.
BCA TU vs. BSc CSIT vs. BIT
-
BCA TU: broad computer applications focus; steady flow from programming to applied business tech; strong project and internship emphasis.
-
BSc CSIT: deeper theory in algorithms, systems, and computing science; math load tends to be higher.
-
BIT: management and information systems flavor with software practice; depends on university.
This quick view helps students align with interest and learning style. For a final pick, compare local campus labs, teaching style, and project support.
Ethics, Law, and Safe Practice
BCA TU includes Cyber Law & Professional Ethics. Treat it as a working toolkit:
-
Credit data and libraries.
-
Use licenses that fit your code.
-
Keep user data private in labs and demos.
-
Write short “limits” notes when you publish a project.
Practical ethics builds trust and protects your work.
On-Campus Learning Tips
-
Sit near peers who ask clear questions. Good questions save time for the class.
-
Before a lab, set one goal and one stretch task.
-
After class, rewrite one tricky idea in five lines.
-
Join one club or coding circle.
-
Present early drafts to a friend in a non-CS course; their feedback improves clarity.
Admissions Steps
-
Visit the FOHSS entrance portal during the notice window.
-
Register with a personal email and phone.
-
Upload the required files as specified on the form.
-
Pay the exam fee through the listed gateway.
-
Track updates from your chosen campus and the FOHSS site.
Check the current cycle for dates and any small rule changes on eligibility bands or document checks.
Real Student Example
A student from a management stream struggled with Math speed. We built a small daily routine:
-
20 minutes of algebra drills.
-
20 minutes of English grammar fixes from a personal error list.
-
20 minutes of GK reading from a single reliable source.
-
A weekly 90-minute mock on Sunday.
Scores rose within four weeks. The student cleared the BCA TU entrance on the first attempt. What changed most was not knowledge; it was steady practice and a written error log tied to the Math 50 / English 40 / GK 10 pattern.
How to Build a Portfolio Semester by Semester
-
Sem 1–2: Small console apps; a basic CRUD app with file storage; one README per repo.
-
Sem 3–4: Data structures visualizer; DBMS mini-project; Project I with a short test plan.
-
Sem 5–6: Web or mobile app with one user flow and a simple analytics note.
-
Sem 7–8: Capstone with two sprints, one user test outside your group, and a 2-minute demo video.
-
Add one page on ethics, licenses, and data handling for the capstone.
Further Study and TNE Context
Graduates who want more theory can try MCA/MIT/MS. Students interested in business paths take MBA with product or analytics. A TNE study for Nepal offers a picture of new learning modes and partnerships, which can sit alongside a TU degree or follow it.
Final Thought
BCA TU offers a clear path from first code to real projects. The program sets a steady pace across eight semesters, then hands you an internship to test your skill in a live setting. Keep your work visible, ask short questions, and treat every project as a public artifact. Small, steady practice wins admissions and builds careers.
FAQs
1) How many credits does BCA TU require?
126 credits across eight semesters. This figure appears in the official TU PDF and across campus handbooks.
2) What is the current entrance weightage?
Mathematics 50%, English Grammar 40%, General Knowledge 10% across 100 objective questions.
3) Where do I apply?
Use the FOHSS entrance portal during the notice window. Follow the steps on the site and track updates.
4) What skills matter most for hiring after BCA?
Clean code, small tests, clear documentation, and a public repo with short case notes. Capstone and internship projects help you show this.
5) What are sensible add-ons to the degree?
Pick one stack-aligned certificate (Java, AWS, Linux, SQL, or CCNA) and build a case study around it. One strong example beats a long badge list.
Tribhuvan University Study in Nepal

