
BSc Computer Science and Information Technology (BSc CSIT), Tribhuvan University (TU)
The Bachelor of Science in Computer Science and Information Technology (BSc CSIT) is one of the most sought-after undergraduate programs under Tribhuvan University (TU) in Nepal. It combines the study of computer science with applied aspects of information technology, preparing students for academic, research, and professional careers in computing and IT services.
In Nepal, where the digital economy is expanding, graduates of this program are playing a key role in software development, IT infrastructure, and global outsourcing markets. The program’s structure is carefully designed to meet both international academic standards and the needs of local industries.
Table of Content
- Overview of the Program
- Objectives of BSc CSIT
- Eligibility Criteria
- Admission Process
- Program Duration and Structure
- Credit Hours and Grading
- Semester-Wise Curriculum
- Electives and Specializations
- Teaching and Evaluation Methods
- Skills Needed to Succeed
- Career Prospects
- Fee Structure of BSc CSIT in Tribhuvan University
- Higher Education Opportunities
- Comparison with Other IT Programs
- Challenges Faced by Students
- Global Relevance of CSIT
- Real-Life Example
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Colleges Offering BSc CSIT (TU) in Nepal
Overview of the Program
BSc CSIT is a four-year degree divided into eight semesters and managed by the Institute of Science and Technology (IOST), TU. Students complete a total of 126 credit hours, including:
-
Core computer science courses such as programming, data structures, and operating systems.
-
Information technology subjects like networking, database systems, and e-governance.
-
Mathematics, statistics, and management courses for analytical and business skills.
-
Electives that introduce emerging areas such as cloud computing, cybersecurity, and mobile application development.
This balance of theoretical and practical learning makes the program relevant both inside Nepal and internationally.
Objectives of BSc CSIT
The main goals of the program are:
-
To build a strong understanding of computing and IT fundamentals.
-
To prepare students to design and develop efficient computer-based systems.
-
To encourage analytical and problem-solving abilities for professional work.
-
To promote research and higher education opportunities.
-
To meet the rising demand for IT professionals in Nepal’s private and public sectors.
Eligibility Criteria
Applicants must meet the following requirements:
-
Completion of 10+2 in Science (or equivalent) with at least a second division.
-
Mathematics as a compulsory subject at the +2 level.
-
Successful performance in the entrance examination organized by IOST.
Because the number of applicants is much higher than the available seats, the entrance exam is highly competitive.
Admission Process
Admission typically involves four steps:
-
Application Form – Students apply through TU-affiliated colleges.
-
Entrance Examination – Covers mathematics, physics, English, and computer fundamentals.
-
Merit List – Published by TU based on exam results.
-
College Enrollment – Selected students complete the final admission process at their chosen college.
Thousands of students compete every year, making preparation for the entrance exam a decisive factor.
Program Duration and Structure
The BSc CSIT program runs for four years across eight semesters. Each semester consists of 90 working days, with theory and practical classes scheduled weekly.
A typical three-credit course includes three hours of lectures and three hours of laboratory work per week. Semester-end examinations are conducted by TU, ensuring uniform academic standards across affiliated colleges.
Credit Hours and Grading
The program is structured into 126 total credit hours. Performance is categorized as:
-
Distinction: 80% and above
-
First Division: 70% and above
-
Second Division: 55% and above
-
Pass Division: 40% and above
Students are required to maintain at least 80% attendance in each course to qualify for examinations.
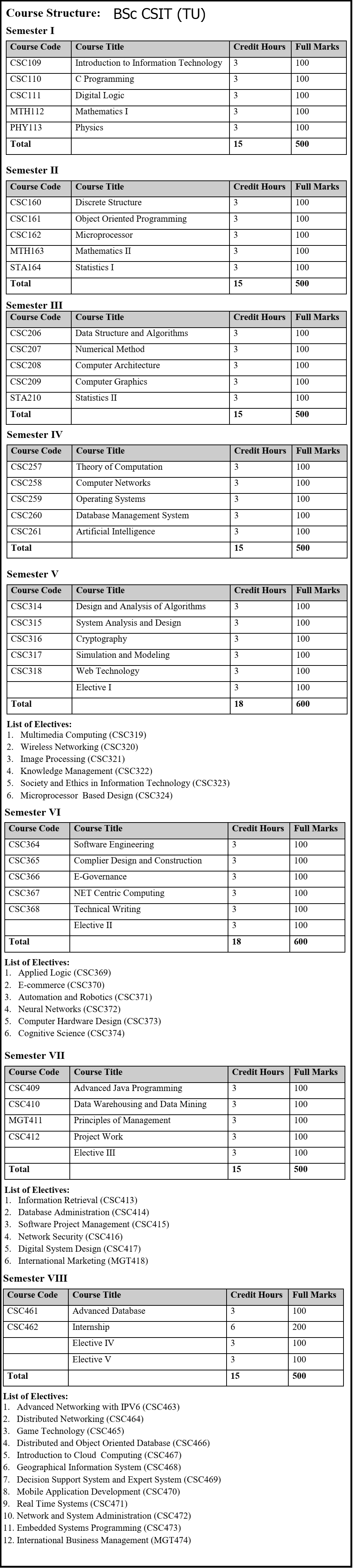
Semester-Wise Curriculum
Semester I – Foundation
-
Introduction to Information Technology
-
C Programming
-
Digital Logic
-
Mathematics I
-
Physics
Semester II – Core Principles
-
Object-Oriented Programming (C++)
-
Discrete Structures
-
Microprocessor
-
Mathematics II
-
Statistics I
Semester III – Programming and Systems
-
Data Structures and Algorithms
-
Numerical Methods
-
Computer Architecture
-
Computer Graphics
-
Statistics II
Semester IV – Networks and AI
-
Theory of Computation
-
Computer Networks
-
Operating Systems
-
Database Management Systems
-
Artificial Intelligence
Semester V – Algorithms and Web Technology
-
Design and Analysis of Algorithms
-
System Analysis and Design
-
Cryptography
-
Simulation and Modeling
-
Web Technology
-
Elective I
Semester VI – Applied IT
-
Software Engineering
-
Compiler Design
-
E-Governance
-
.NET Centric Computing
-
Technical Writing
-
Elective II
Semester VII – Advanced Studies
-
Advanced Java Programming
-
Data Warehousing and Data Mining
-
Principles of Management
-
Project Work
-
Elective III
Semester VIII – Internship and Specializations
-
Advanced Database
-
Internship (6 credits)
-
Electives IV and V
The curriculum encourages both academic rigor and workplace readiness, with students required to complete a final-year internship.
Electives and Specializations
Students can choose electives from a wide range of subjects, allowing them to specialize in specific areas. Options include:
-
Artificial Intelligence and Robotics
-
Cybersecurity and Network Administration
-
Mobile Application Development
-
Cloud Computing
-
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
-
Game Technology
Electives help students align their studies with career aspirations or further academic pursuits.
Teaching and Evaluation Methods
Evaluation combines internal assessment and final examinations:
-
Internal evaluation (20%) includes class tests, assignments, and participation.
-
Final examinations (80%) are administered by TU.
-
Practical courses and labs include separate evaluations.
-
Final-year project and internship are assessed by both internal and external examiners.
This method ensures both continuous engagement and standardized academic testing.
Skills Needed to Succeed
Students who excel in the program often develop:
-
Strong mathematical reasoning and analytical skills.
-
Proficiency in programming languages such as C, C++, Java, and Python.
-
Ability to work with databases and networks.
-
Teamwork and communication skills for collaborative projects.
-
Adaptability to rapidly changing IT tools and environments.
Career Prospects
Graduates of BSc CSIT are employed in a wide range of roles:
-
Software Developer – Building applications and enterprise systems.
-
Database Administrator – Managing large-scale information systems.
-
Network Engineer – Designing and maintaining IT networks.
-
Data Analyst – Using statistics and computing to generate insights.
-
Cybersecurity Officer – Securing digital infrastructures.
-
Government IT Officer – Serving through Public Service Commission examinations.
-
Researcher or Lecturer – Contributing to academia and innovation.
The private sector—especially banking, telecommunications, fintech, and outsourcing—regularly hires CSIT graduates. Many students also work remotely for companies in the USA, Europe, and Asia.
Fee Structure of BSc CSIT in Tribhuvan University
The cost of studying BSc CSIT under Tribhuvan University varies depending on whether a student is enrolled in a constituent campus (directly run by TU) or a private TU-affiliated college.
-
Constituent Campuses (e.g., Amrit Science Campus, Patan Multiple Campus): The fee is relatively affordable, generally ranging from NPR 2.5 to 3.5 lakhs for the entire four-year program. These campuses are highly competitive, with limited seats.
-
Private TU-Affiliated Colleges: Fees are higher compared to constituent campuses. On average, students pay NPR 6 to 8 lakhs for the complete program. Some institutions with better infrastructure and facilities may charge slightly more.
Factors Affecting Fee Variation:
-
Type of college (government vs. private affiliation).
-
Availability of laboratory facilities, libraries, and student support services.
-
Location of the campus (Kathmandu Valley colleges usually charge higher fees).
The overall cost still remains reasonable compared to international IT degrees, making BSc CSIT a preferred choice for students across Nepal.
Higher Education Opportunities
Graduates often continue to advanced studies such as:
-
MSc CSIT offered by Tribhuvan University.
-
Master’s programs in computer science, data science, or artificial intelligence abroad.
-
Professional certifications including Cisco (CCNA), AWS, Microsoft, or PMP to strengthen industry credentials.
Comparison with Other IT Programs
| Degree | Focus | Career Pathways |
|---|---|---|
| BSc CSIT | Combination of theory and applied IT | Technical careers, higher studies, research |
| BIT | Practical IT and system management | Industry-ready jobs in IT companies |
| BCA | IT with business applications | IT in business, management, and corporate systems |
Challenges Faced by Students
Common challenges include:
-
Entrance exam competition – Thousands apply for limited seats.
-
Workload – Balancing demanding coursework in mathematics, programming, and labs.
-
Infrastructure gaps – Not all colleges have updated laboratories.
-
Self-study needs – Success often requires independent learning beyond classroom hours.
Global Relevance of CSIT
Nepal’s IT outsourcing industry is growing steadily. According to World Bank reports, digital services in South Asia are becoming an important export sector. Nepali CSIT graduates are contributing to global companies in software engineering, mobile development, and data analysis.
This international adaptability proves the long-term value of the TU BSc CSIT program.
Real-Life Example
A graduate from TU’s CSIT program, who started as a local software intern in Kathmandu, is now working remotely for a European data analytics firm.
His project experience during the final semester and elective courses in data mining gave him the confidence and skill set needed to compete internationally. Stories like this highlight the program’s practical benefits for motivated students.
Conclusion
BSc CSIT at Tribhuvan University offers a strong foundation in computer science and information technology, preparing students for academic, professional, and global opportunities.
Its balanced curriculum, competitive admission, and focus on both theory and practice make it one of the most respected IT degrees in Nepal. For students seeking a career in computing, this program provides both immediate and long-term pathways for growth.
FAQs
1. What is the fee structure for BSc CSIT in TU-affiliated colleges?
The fee varies by institution but generally ranges from NPR 3 to 6 lakhs for the full program.
2. Is mathematics mandatory for admission?
Yes. Students must have studied mathematics in their +2 or equivalent level.
3. What kinds of jobs are available after graduation?
Graduates can work as software developers, IT officers, database administrators, or network engineers in both the public and private sectors.
4. How competitive is the CSIT entrance exam?
It is highly competitive, with thousands of students competing for limited seats every year.
5. Can CSIT graduates work internationally?
Yes. Many graduates pursue further studies abroad or secure jobs in international IT companies through outsourcing or remote work opportunities.
Colleges Offering BSc CSIT (TU) in Nepal
Jhapa
-
Mechi Multiple Campus – Bhadrapur
-
Shreeyantra College – Damak
Morang
-
Mahendra Morang Adarsha Multiple Campus – Biratnagar
-
AIMS College – Biratnagar
-
Birat Kshitiz College – Biratnagar
-
Birat Multiple College – Biratnagar
-
Himalaya Darshan College – Biratnagar
-
Niharika College – Biratnagar
Sunsari
-
Central Campus of Technology – Dharan
-
Birendra Memorial College – Dharan
-
Godawari College – Itahari
Dhanusha
-
Ramsorup Ramsagar Multiple Campus – Janakpur
Bara
-
National Infotech College – Birgunj
Chitwan
-
Birendra Multiple Campus – Bharatpur
-
Chitwan College of Technology – Bharatpur
Makawanpur
-
Hetauda City College – Hetauda
Dang
-
Ambikeshwori Information & Technical Campus – Ghorahi
-
Mahendra Multiple Campus – Dang
Banke
-
Mahendra Multiple Campus – Nepalgunj
-
Bake Bageshwori College – Nepalgunj
-
Nepalgunj Campus – Nepalgunj
Rupandehi
-
Butwal Multiple Campus – Butwal
-
Bhairahawa Multiple Campus – Bhairahawa
-
Lumbini City College – Butwal
-
Nepathya College – Butwal
Palpa
-
Tribhuvan Multiple Campus – Palpa
Kaski
-
Prithivi Narayan Multiple Campus – Pokhara
-
Mount Annapurna Campus – Pokhara
-
Soch College of IT – Pokhara
Kavre
-
NIST College – Banepa
Kathmandu
-
Amrit Campus – Lainchour
-
Padma Kanya Multiple Campus – Bagbazar
-
Ambition College – Baneshwor
-
Asian School of Management & Technology – Samakhushi
-
College of Applied Business & Technology – Gangahity, Chabahil
-
Deerwalk Institute of Technology – Sifal
-
Himalaya College of Engineering – Shankhamul
-
Kathmandu BernHardt College – Bafal
-
Madan Bhandari Memorial College – Anamnagar
-
National College of Computer Studies – Paknajol
-
Nepalaya College – Kalanki
-
New Summit College – Purano Baneshwor
-
Orchid International College – Sinamangal
-
Prime College – Nayabazar, Khusibu
-
St. Lawrence College – Chabahil
-
St. Xavier’s College – Maitighar
-
Texas International College – Chabahil
-
Trinity International College – Dillibazar
Lalitpur
-
Patan Multiple Campus – Patan
-
Academia International College – Gwarko
-
Asian College of Higher Studies – Jawalakhel
-
Kathford Int. College of Engineering and Management – Lalitpur
-
Nagarjuna College of IT – Pulchowk
-
Sagarmatha College of Science & Technology – Sanepa
-
Vedas College – Jawalakhel
Bhaktapur
-
Bhaktapur Multiple Campus – Bhaktapur
-
Kathmandu College of Technology – Lokanthali
-
Samridhi College – Lokanthali
-
Swastik College – Thimi
Kanchanpur
- Sidha Nath Science Campus – Mahendranagar
Nawalparasi
- Lumbini ICT College – Gaidakot, Nawalparasi
Download
BSc CSIT Course Syllabus (TU).PDF![]()


