Overview
Pokhara Metropolitan City (पोखरा महानगरपालिका / Pokhara Mahanagarpalika) was established in May 2017 as a local government of Nepal. Its headquarters are located in New Road, Pokhara, Kaski district, Gandaki Province of Nepal. Pokhara is a Metropolitan city known as Mahanagarpalika in the Nepali Language. It is the second largest city in terms of population after the Capital city, Kathmandu.

Geographic and Administrative Significance
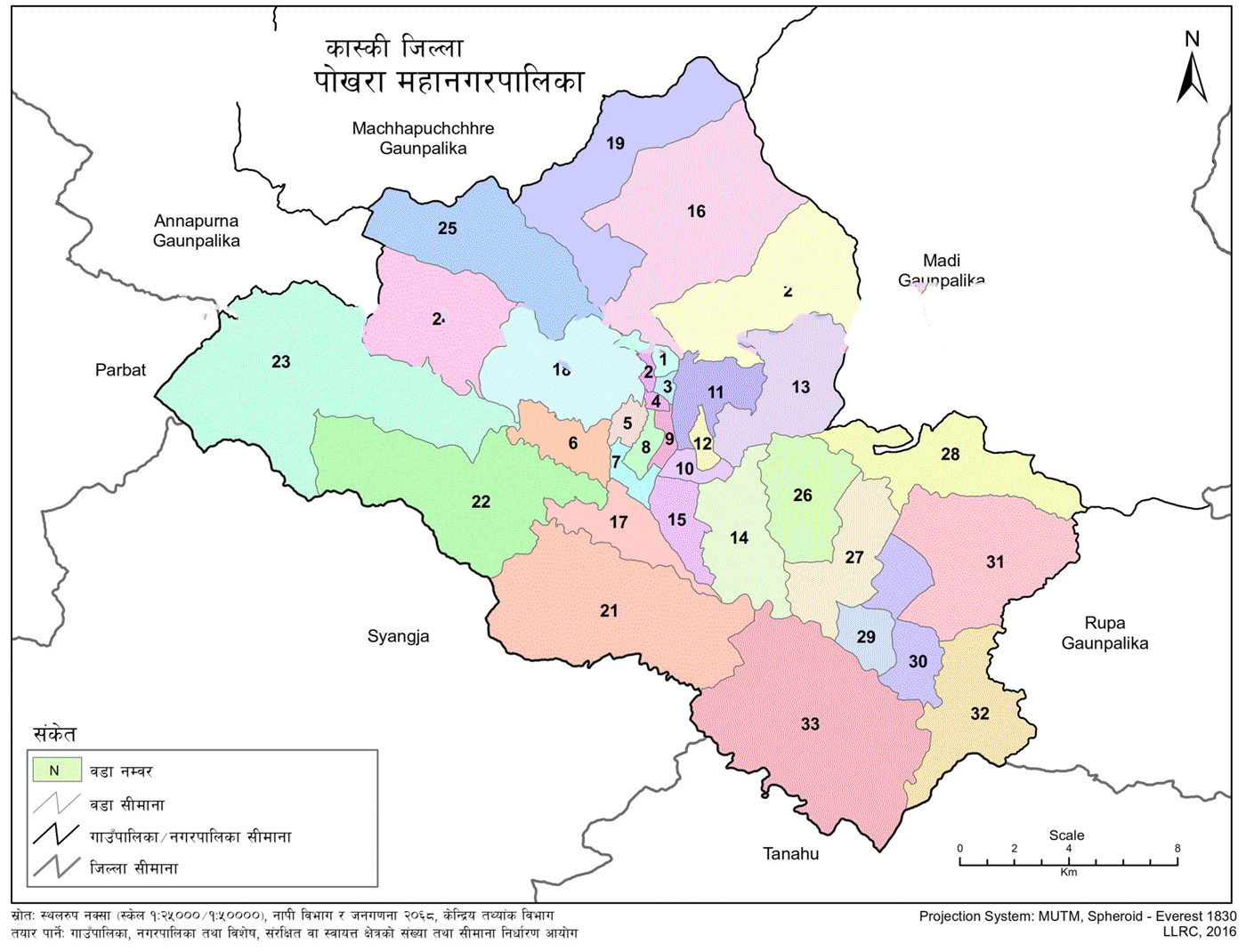
Pokhara Metropolitan City is the largest metropolitan city in Nepal in terms of area. It encompasses a diverse geographical landscape with 33 ward offices, 170 elected representatives, around 800 employees (excluding teachers), and over 500,000 permanent residents. An equally large number of people reside temporarily, and the city also handles the direct and indirect management of approximately 600,000 domestic and 500,000 foreign tourists annually.
As the capital of Gandaki Province, Pokhara's beauty, management, and development are now of concern to the citizens of all 11 districts within the province. With Nepal recently embracing federalism, Pokhara’s activities as a local government are closely monitored. This scrutiny necessitates the city to deliver notable and distinctive outcomes. The success or failure of Pokhara is seen as indicative of the overall success or failure of federalism and local governance in Nepal, placing greater responsibility on the city.
| Category | Detail |
| City Type | Largest metropolitan in Nepal by area (464.24 sq. km) |
| Population | 513,504 (Census 2078 BS) |
| Wards | 33 administrative wards |
| Employees | Around 800 (excluding teachers) |
| Elected Representatives | 170 |
| Tourist Influx | 600,000 domestic & 500,000 international tourists annually |
| Provincial Status | Capital of Gandaki Province |
| Judicial System | Three-member Judicial Committee under the Deputy Chief |
| Public Accounts | Committee formed per the Local Government Act 2074 BS |
| Reform Focus | Service decentralization, ward-level empowerment, and rule enforcement |
| Cultural Attractions | Temples, monasteries, caves, museums |
| Natural Attractions | Rivers, lakes, parks, and botanical gardens |
| Adventure Tourism | Paragliding, trekking, zip flyer, bungee jump |
| Tourist Routes | Over 20 local and extended trekking/ travel circuits |
Historical Evolution of Pokhara Metropolitan
Originally established as a municipality in 2016 BS with 13 wards, Pokhara expanded in 2052 BS to become a sub-metropolitan city with 18 wards. After the establishment of the republic, on 16th Mangsir 2071 BS, Pokhara was transformed into a sub-metropolitan city with 29 wards by merging adjacent Village Development Committees (VDCs).
Following the promulgation of the Constitution in 2072 BS and subsequent restructuring of the state, the previous Pokhara sub-metropolitan city, Lekhnath municipality, and several surrounding VDCs were merged to create Pokhara Lekhnath Metropolitan City with 33 wards on 27th Falgun 2073 BS. The Government of Nepal officially renamed it Pokhara Metropolitan City on 23rd Shrawan 2075 BS based on the city council’s recommendation.
Area and Population
The total area of Pokhara Metropolitan City is 464.24 square kilometers. According to the preliminary results of the National Census 2078 BS, the population is 513,504. The administrative center remains at the former Pokhara sub-metropolitan office.
The city is bordered by Madi and Rupa rural municipalities to the east, Annapurna rural municipality, Parbat, and Syangja districts to the west, Machhapuchhre and Madi rural municipalities to the north, and Syangja and Tanahun districts to the south.
Judicial Committee
According to Article 217 of Nepal’s Constitution, a judicial committee is established as a constitutional body at the local level. As Nepal transitions into a federal system with three levels of government – federal, provincial, and local – judicial committees serve as the judiciary at the local level. These committees are formed under the coordination of the deputy chief and consist of three members to resolve disputes within the local government's jurisdiction.
The Local Government Operation Act, 2074 BS, particularly Chapter 8, Sections 46 to 53, outlines judicial committees' formation, jurisdiction, and operation. Following these provisions, Pokhara has formed a judicial committee, which began its function following the tenth city council session.
Public Accounts Committee
Section 22 of the Local Government Operation Act, 2074 BS, mandates forming a public accounts committee at the local level. Pokhara Metropolitan City has also complied with the 2076 BS procedure for forming its public accounts committee as required by law.
Reform Initiatives in Pokhara Metropolitan
Reforms must start with oneself and begin immediately. Criticizing others is easy; changing oneself is the hardest. Pokhara Metropolitan has prioritized internal management and reform. The focus is on establishing good governance through efficient service delivery and development management.
Efforts are made to implement federal principles by delivering public services at the local level. Daily services are provided through respective ward offices, allowing the central office to focus on legislation, planning, monitoring, evaluation, and coordination.
Policies have been introduced allowing residents to:
-
Pay all taxes at the ward office
-
Complete house blueprint approvals (up to 1,000 sq ft and three floors) at the ward
-
Finalize all ward-level project agreements through consumer committees
-
Register and renew businesses, firms, and community groups at the ward
-
Obtain senior citizen ID cards and social security benefits from the ward offices
Improvements include enhancing the physical infrastructure of ward offices, constructing new office buildings, upgrading facilities and IT resources, and deploying more staff. Due to necessity, many employees have been reassigned from the central office to the wards. Staff conduct and discipline are closely monitored, and disciplinary actions are taken accordingly.
Rules are strictly enforced without exception, favoritism is rejected, and a firm stance is taken against using political affiliations for negligence or misconduct. A staff bus service has been introduced for employee convenience. Based on clear policies and strategic plans, further improvements are underway for sanitation and market management.
Key Natural, Religious, Cultural, and Tourist Attractions in Pokhara

Rivers and Streams
-
Seti River
-
Surya Khola
-
Kaun Khola
-
Phurse Khola
-
Harpan Khola
-
Yamdi Khola
-
Vijayapur Khola
-
Bulaundi Khola
-
Kali Khola
-
Gadwa Khola
Lakes and Ponds
-
Phewa Lake
-
Begnas Lake
-
Rupa Lake
-
Maidi Lake
-
Khaste Lake
-
Gunde Lake
-
Nyureni Lake
-
Dipang Lake
-
Panchase Lake
-
Kashyap Lake
-
Lotus Pond
Temples, Shrines, Monasteries
-
Bindhyabasini Temple
-
Tal Barahi Temple
-
Bhadrakali Temple
-
Akaladevi Temple
-
Kedareshwar Temple
-
Gupeshwar Mahadev Temple
-
Narayansthan Temple
-
Geeta Temple
-
Ram Temple, Ramghat
-
Kotedhunga Bhartipo Khari Temple
-
Sada Shiva Temple, Dhungesangu
-
Laxmi Narayan Temple, Amala
-
Shova Bhagwati Temple, Ranipauwa
-
Siddheshwar Mahadev Temple, Fulbari
-
Guptakalika Temple, Kaskikot
-
Tulakot Temple
-
World Peace Stupa, Anadu Hill
-
Matepani Monastery
-
Hemja Monastery
-
Dharma Shila Buddha Monastery, etc.
Forts, Towers, and Viewpoints
-
Sarangkot View Tower
-
Kaun Tower
-
Mohariya View Tower
-
Panchase View Tower
-
Sundari Danda View Tower
-
Hudikot
-
Pumdikot
-
Amala Kot
-
Bhurjungkot
Caves
-
Mahendra Cave
-
Chamero Cave
-
Harihar Cave
-
Gupeshwar Cave, Bhalam
-
Siddha Cave
-
Sita Cave and others
-
Kaskikot Palace
-
Rata Temple, Barahichaur
-
Davis Falls, etc.
Museums
-
International Mountaineering Museum
-
Gorkha Museum
-
Pokhara Memorial Museum
-
Regional Museum
-
Important Puppet Museum
Adventure and Sports Tourism
-
Paragliding
-
Zip Flyer
-
Bungee Jump
-
Trekking
-
Ultra-light Flight
-
Hiking
-
Pony Trek
-
Yachting
-
Fishing
-
Football, Volleyball, Cricket, including international events
Parks, Gardens, Botanical Areas
-
Komagane Friendship Park
-
Basundhara Park
-
Children's Park
-
Fulbari Park
-
Manakamana Park
-
Shanti Ban Garden, etc.
Tourism and Pokhara
Pokhara Metropolitan City is prominent among Nepal’s largest metropolitan areas due to its unique geography and strategic significance. Known as the gateway to several renowned tourist destinations and home to cultural and natural heritage, the city plays a vital role in the tourism industry.
Tourism in Pokhara involves structured development initiatives, infrastructure planning, and diverse promotion campaigns, all guided by an overarching vision. Pokhara has implemented targeted tourism policies to promote and preserve this identity, including road improvements, lakeshore management, traffic regulation, sanitation, development of spiritual sites, and protection of cultural assets.
Additional projects include:
-
Road repairs and streetlight installations
-
Proper traffic and transport management
-
Clean market zones for fish, meat, water, and telecom services
-
Parking space management
-
Construction of tourism information centers
-
Waste management programs
-
Promotion of religious and historical sites
-
Development of local agricultural markets
-
Branding of the Seti River as a tourism asset
-
Development of photography spots
-
Temple and monument maintenance
-
Restoration of heritage sites
-
Establishment of public restrooms
-
Construction of tourist accommodations
Tourism routes originating from Pokhara and connecting nearby destinations include:
-
Pokhara-Panchase
-
Pokhara-Ghachowk-Pokhara
-
Pokhara-Trek-Bharabhari-Pokhara
-
Pokhara-Beni-Jomsom-Pokhara
-
Pokhara-Gurung Heritage-Pokhara
-
Pokhara-Dam Side-Kahun-Pokhara
-
Pokhara-Kaskikot-Pokhara
-
Pokhara-Sarangkot-Pokhara
-
Pokhara-Begnas-Pokhara
-
Pokhara-Rupakot-Pokhara
-
Pokhara-Sikles-Pokhara
-
Pokhara-Siranchaur-Milanchok-Dhital
-
Pokhara-Bharabhari-Sirubari
-
Pokhara-Baglung-Pokhara
-
Pokhara-Khoramukh-Namche-Pokhara (Mardi Trek)
-
Pokhara-Birethanti-Pokhara
-
Pokhara-Nagdada-Pokhara
-
Pokhara-Kalikastan-Pokhara
-
Pokhara-Bharabhari-Rupakot-Pokhara (Resort Trek)
-
Pokhara-Manang
Pokhara is dedicated to becoming a top-tier international tourist destination and has implemented master plans to develop sustainable, community-based, and eco-friendly tourism infrastructure.




