Overview
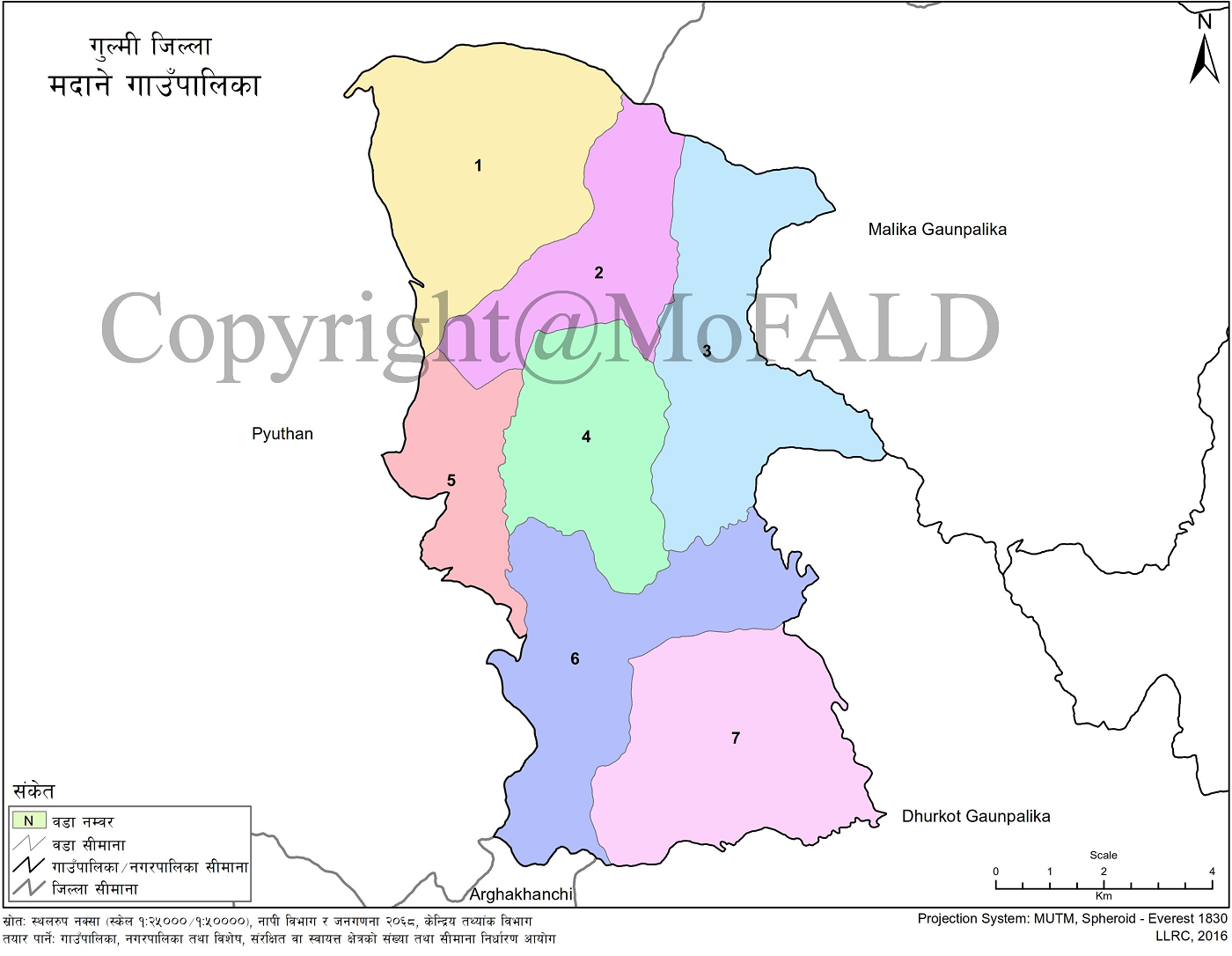
Madane Rural Municipality (Gaupalika - मदाने गाउँपालिका, गुल्मी): Situated at the highest point of Gulmi district, Madane features the renowned Madane hill, standing at an elevation of 3,200 feet above sea level. The area is home to a diverse array of herbs, birds, and wildlife. Nearly all wards of Madane Rural Municipality lie on the eastern side of this hill, except Ward No. 1, which is located on the western side.
Malika and Dhurkot Rural Municipalities border it to the east; Gaumukhi and Jhimruk Rural Municipalities of Pyuthan District to the west; Malika Rural Municipality and Gaumukhi Rural Municipality of Pyuthan District to the north; and Dhurkot Rural Municipality to the south. This biodiverse municipality ranges from 1,000 meters to 2,690 meters above sea level and is primarily agricultural in land use.
Historical Background and Naming
With the Madane summit and Kankedeurali as major tourist attractions, the region offers natural beauty with rivers like Panah and Jhimruk originating from Madane. As a boundary region between Gulmi, Arghakhanchi, and Pyuthan districts, it also holds historical significance. The breathtaking views from Kankedeurali and Shaire Lake's green hills and villages contribute to internal tourism. The area historically included Sanipokhari, an old boundary during the Chaubise kingdom era, still recognized today.
Political Formation
Madane Rural Municipality was established on Falgun 27, 2073 BS. It consists of the following seven wards formed from previous Village Development Committees (VDCs):
-
Ward No. 1: Aglung (1–9)
-
Ward No. 2: Banjhkateri (1–9)
-
Ward No. 3: Sirsheni (1–9)
-
Ward No. 4: Myalpokhari (1–9)
-
Ward No. 5: Lagiri (1–9)
-
Ward No. 6: Purkot Daha (1–9)
-
Ward No. 7: Bhanbhane (1–9)
Area
The total area of Madane Rural Municipality is 94.52 sq. km. It is composed of the former VDCs: Aglung, Banjhkateri, Sirsheni, Myalpokhari, Malagiri, Purkot Daha, and Bhanbhane.
Climate and Weather
Located in the western part of the district, Madane has an elevation ranging from 1,000 to 2,690 meters. The climate is subtropical monsoon, characterized by moderate temperatures, cool winters, and warm summers. The warm season lasts from March to October, while November to February is the colder season. The coldest months are December and January, and the hottest month is May. The area receives an average annual rainfall of 2,200 mm, and the average yearly temperature is 27°C.
Cultural Richness
Festivals and cultural practices are tied to ethnic and religious identity. The traditions here are long-standing and specific to different communities, representing a blend of religious and cultural values.
Population Details
Population is the foundation of a state. Without it, no form of governance or development is possible. It drives development and governance, so accurate demographic data is essential. In Madane Rural Municipality, the total population is 27,176:
-
Male: 13,962
-
Female: 13,214
This population data supports planning and service delivery across the municipality.
Language
Language is the medium of expression and a core part of local identity and culture. While Nepal is home to 123 languages, Madane Rural Municipality is predominantly Nepali-speaking, with 100% of the population using Nepali as their mother tongue.
Religion
Despite the presence of diverse ethnic groups, Hinduism is the dominant religion followed by almost all residents of the municipality.
Ethnic Composition
Nepal is known for its ethnic diversity, and Madane is no exception. With over 125 ethnic groups and 123 languages nationwide, Madane also reflects this mosaic of cultures and communities, contributing to Nepal's rich heritage.
Key Agricultural Activities
Special Pocket Farming and Main Crops
-
Pocket Areas
-
Maize seed production in Ward No. 6 (Purkot Daha) and Ward No. 7 (Bhanbhane Badachaur).
-
Core production areas: Harrabot and Badachaur.
-
Millet, honey, and potato are also cultivated under this category.
-
-
Commercial Farming
-
Goat farming is practiced as a commercial activity.
-
Some farmers are involved in small-scale poultry farming.
-
Ginger and potato pocket zones have been identified in Ward No. 1 (Aglung) and Ward No. 2 (Banjhkateri).
-
Notable production of millet and maize is also recorded, with exports taking place.
-
Residents in border areas often use roads via Pyuthan to access locations other than the district headquarters in Tamghas.
Tourism Development
Tourism relates to travel. In earlier times, people traveled for trade and pilgrimage. Later, travel itself became commercialized, evolving into tourism. Over time, tourism has grown to become a significant economic activity.
Tourism involves a person's activities within a specific country, region, or city for economic and recreational purposes. A person traveling within their own country also qualifies as a tourist if the journey involves spending and contributes to the local economy.
Tourism is classified into two main types:
-
Domestic Tourism: Travel within the same country.
-
International Tourism: Travel from one country to another.
Tourism directly supports hotel businesses, local services, and the national economy.
Tourist and Host Relationship
Tourism involves both tourists and hosts. A tourist (guest) visits new locations and avails services, while the host (local) provides services in exchange for money. If a traveler carries everything and doesn’t spend locally, it’s travel, not tourism.
A stay of at least 24 hours in a different location is typically required for tourism.
Attractions That Influence Tourism
Tourists are drawn to specific features of a place. These pull factors include:
-
Natural features: Lakes, rivers, snow, waterfalls, hills, valleys
-
Cultural elements: Festivals, traditional songs, crafts, costumes
-
Manmade attractions: Museums, monuments, religious sites, sports events
-
Hospitality, safety, shopping areas, exhibitions, and peace also play roles.
Types of Tourists and Tourism
Tourism types vary based on tourist intentions. Some key categories include:
1. Adventure Tourism
-
Mountain climbing
-
Rock climbing
-
Bungee jumping
-
White-water rafting
-
Ballooning
Nepal’s mountainous regions attract thousands of adventure tourists each year.
2. Dark Tourism
-
Visits to sites of wars, natural disasters, and major accidents (e.g., tsunami sites)
-
Tourists seek to witness damage and learn about the events
3. Recreational Tourism
-
Tourists travel for fun, relaxation, and leisure
-
Natural beauty, landscapes, rivers, forests, and local biodiversity attract these tourists
4. Holiday or Leisure Tourism
-
For rest, amusement, and rejuvenation
-
Includes nature trips, visits to historic places, cultural exposure
5. Cultural Tourism
-
Visits to cultural and historical sites
-
Tourists learn about different communities, religions, lifestyles, clothing, and customs
6. Business Tourism
-
Travel related to commerce, industry, or professional conferences
7. Religious Tourism
-
Visits to spiritual destinations like Kashi, Gaya, Haridwar, Muktinath, Lumbini, Jerusalem
-
The largest volume of global tourists fall under this category
8. Sports Tourism
-
Travel to watch or participate in national/international sporting events like the Olympics, World Cup
9. Medical Tourism
-
Travel for medical checkups and treatment
-
Developed countries attract patients from less equipped regions
Broad Perspective on Tourism
People travel for diverse reasons—leisure, culture, business, spirituality, health. Thus, the forms of tourism are varied and expanding. Governments and tourism bodies now organize services based on tourist interests to maximize foreign currency earnings.
A tourist can often belong to multiple categories at once—for example, a pilgrim can also be a cultural or holiday tourist. Similarly, an adventure tourist may also have cultural interests. Therefore, tourism cannot be limited to a single definition or activity.
Tourism thrives not only in beautiful or developed areas but also in places with minimal infrastructure, depending on what the traveler seeks. Tourists from well-developed countries may seek natural experiences, while those from less developed regions may be drawn to man-made environments.
In conclusion, tourism is multifaceted and must be understood through the various purposes and interests that drive people to travel.
Schools in Madane Rural Municipality
Summary
-
Pre-school Level: 43
-
Basic Schools: 47
-
Secondary Schools: 8
-
Plus-2 Programs: 2
-
Public Schools: 47
-
Private Schools: 2
-
Total Institutions: 49
Pre-schools (Nursery Level Schools)
-
Purkot Bright Future Academy — Nursery–7, Madane, Gulmi
-
A G Bright Future Academy — Nursery–3, Madane, Gulmi
-
Kanke Deurali Lower Secondary School — Nursery–8, Madane, Gulmi
-
Banjhakateri Meghaganga Secondary School — Nursery–10, Madane, Gulmi
-
Mehalepokhari Secondary School — Nursery–10, Madane, Gulmi
-
Riyale Secondary School — Nursery–12, Madane, Gulmi
-
Aglung Secondary School — Nursery–10, Madane, Gulmi
-
Pura Secondary School — Nursery–10, Madane, Gulmi
-
Shree Okhledaha Basic School — Nursery–8, Madane, Gulmi
-
Raghuphedi Partima Nima Secondary School — Nursery–10, Madane, Gulmi
-
Balbikash Lower Secondary School — Nursery–8, Madane, Gulmi
-
Timurkharka Basic School — Nursery–8, Madane, Gulmi
-
Dipak Secondary School — Nursery–10, Madane, Gulmi
-
Bal Bikash Basic School — Nursery–5, Madane, Gulmi
-
Dharachaur Basic School — Nursery–8, Madane, Gulmi
-
Khanyukharka Lower Secondary School — Nursery–8, Madane, Gulmi
-
Janak Lower Secondary School — Nursery–8, Madane, Gulmi
-
Ghaderi Basic School — Nursery–5, Madane, Gulmi
-
Janasewa Lower Secondary School — Nursery–8, Madane, Gulmi
-
Malika Basic School — Nursery–3, Madane, Gulmi
-
Mulpani Basic School — Nursery–3, Madane, Gulmi
-
Araniko Basic School — Nursery–3, Madane, Gulmi
-
Sirseni Basic School — Nursery–5, Madane, Gulmi
-
Harre Basic School — Nursery–5, Madane, Gulmi
-
Banjh Kateri Basic School — Nursery–5, Madane, Gulmi
-
Siddhartha Basic School — Nursery–5, Madane, Gulmi
-
Surjyang Basic School — Nursery–5, Madane, Gulmi
-
Balkalyan Basic School — Nursery–3, Madane, Gulmi
-
Baraha Basic School — Nursery–3, Madane, Gulmi
-
Balbodh Primary School — Nursery–3, Madane, Gulmi
-
Sibalaya Basic School — Nursery–3, Madane, Gulmi
-
Nawa Durga Basic School — Nursery–3, Madane, Gulmi
-
Janajyoti Basic School — Nursery–3, Madane, Gulmi
-
Bal Kalyan Basic School — Nursery–3, Madane, Gulmi
-
Namuna Basic School — Nursery–3, Madane, Gulmi
-
Jana Chahana Basic School — Nursery–3, Madane, Gulmi
-
Laligurash Basic School — Nursery–3, Madane, Gulmi
-
Sidda Pokhari Basic School — Nursery–3, Madane, Gulmi
-
Bal Sundar Basic School — Nursery–1, Madane, Gulmi
-
Bhagawati Basic School — Nursery–Nursery, Madane, Gulmi
-
Siddha Malika Bal Bikas Kendra — Nursery–Nursery, Madane, Gulmi
-
Patalkateri Basic School — Nursery–1, Madane, Gulmi
-
Tindhare Basic School — Nursery–2, Madane, Gulmi
Basic Level Schools (Nursery–Grade 5 or 8)
-
Panchami Pokhari Basic School — Grade 1–5
-
Sherr Topre Aadharabhut School — Grade 1–5
-
Jana Kalyan Basic School — Grade 2–5
-
Madane Bal Kalyan Basic School — Grade 1–3
-
Bal Netra Jyoti Basic School — Grade 4–5
Secondary and Plus-2 Level Schools
-
Prithivi Secondary School Madane Gulmi
-
Grades 1–12
-
Affiliated with the National Examinations Board
-
Location: Purkotdaha, Madane, Gulmi
-









