
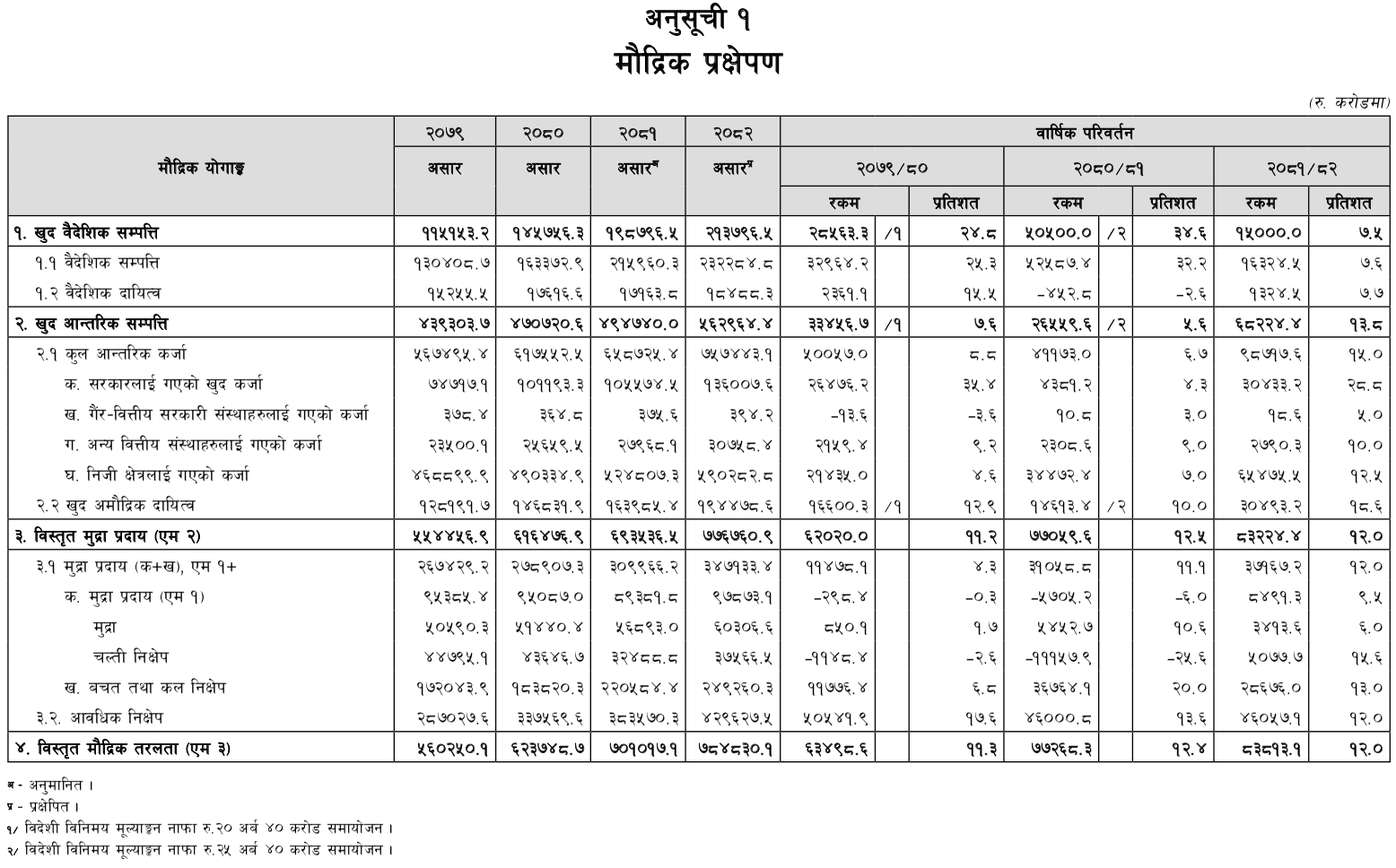
Nepal's Monetary Policy for Fiscal Year 2081/082: Key Highlights and Objectives
The Government of Nepal has introduced its monetary policy for the fiscal year 2081/082. Governor Maha Prasad Adhikari of the Nepal Rastra Bank presented the policy on 2081 Shrawan 11.
Cautious and Flexible Approach
Governor Adhikari stated that the new policy continues a cautious and adaptable approach to ensure economic dynamism. The focus is on maintaining financial stability while enhancing credit flow to productive sectors and improving loan quality.
Alignment of Policies
There is a coordinated effort to align monetary and regulatory policies, ensuring that credit flow is facilitated without compromising macroeconomic stability.
Fixed Exchange Rate and Inflation Control
The policy retains the fixed exchange rate of the Nepali rupee with the Indian rupee. Additionally, measures are in place to manage monetary expansion to keep inflation around 5.0 percent, preventing undue price pressures.
Foreign Exchange Reserves and Economic Growth
Key objectives include:
- Maintaining foreign exchange reserves sufficient for at least 7 months of imports.
- Keeping the weighted average interbank rate close to the policy rate through rule-based open market operations.
- Directing liquidity and credit flow towards productive sectors to achieve an economic growth rate of 6.0 percent.
Interest Rate Adjustments
- The upper limit of the interest rate corridor (bank rate) is reduced from 7 percent to 6.5 percent.
- The policy rate is lowered from 5.5 percent to 5.0 percent.
- The deposit collection rate, the lower limit of the interest rate corridor, remains at 3.0 percent.
Liquidity and Regulatory Provisions
The provision for a permanent liquidity facility at the bank rate will continue, with more flexible conditions for accessing permanent liquidity. Existing provisions regarding the mandatory cash ratio and statutory liquidity ratio for banks and financial institutions are also maintained.
Foreign Exchange Policy Adjustments
With increasing foreign currency reserves, the Nepal Rastra Bank has relaxed its stringent foreign exchange policy. New measures include:
- Higher limits on foreign exchange via passports.
- Increased limits for foreign exchange through drafts and TTs for imports, from $35,000 to $50,000.
- Raised limits for imports from $60,000 to $100,000.
- More flexible payment limits from convertible accounts opened in Nepal.
Gold and Silver Import Review
The Nepal Rastra Bank will review existing provisions related to the import and distribution of gold and assess the current status of silver imports.
Asset Management Initiatives
To manage non-performing and non-banking assets of financial institutions, a draft of the Asset Management Company Act will be formulated to establish an asset management company.
This policy aims to foster a stable and dynamic economic environment by balancing regulatory measures and facilitating productive financial activities.
Download Monetary Policy 2081/082.PDF![]()





