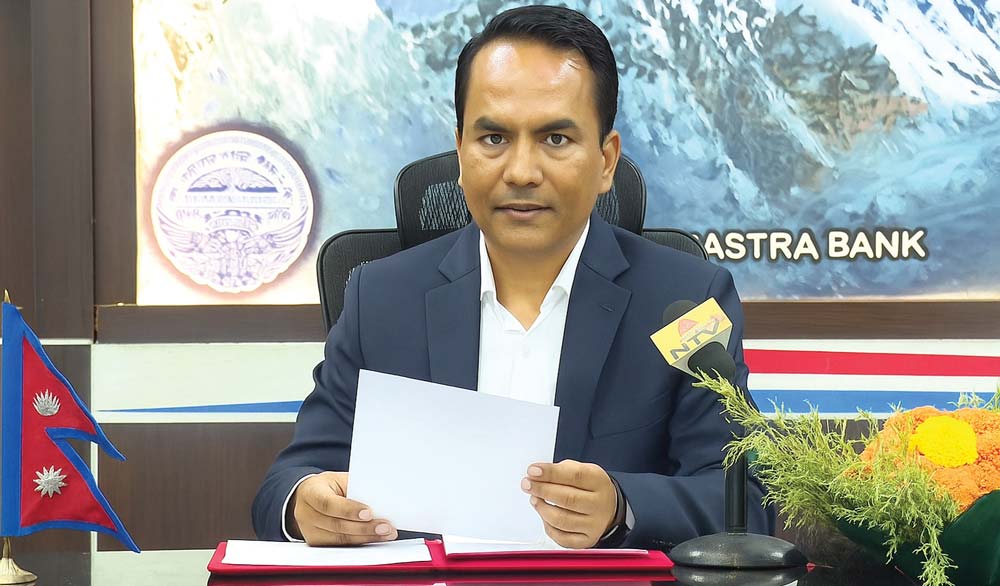
Education Sector Support under the Monetary Policy 2082/83
The Monetary Policy 2082/83 includes key provisions that directly support the education sector, especially through credit access and regulatory reforms:
Working Capital Loan Adjustments:
The policy states that the guidelines related to working capital loans will be revised based on the income cycle and nature of specific sectors. This includes education, along with agriculture, media, sports, and health.
These adjustments allow educational institutions—such as schools, colleges, and training centers—to align their loan repayment schedules with their actual revenue flows, particularly those that rely on periodic student enrollments.
Loan Structuring Based on Revenue and Expense Cycles:
Educational institutions often have seasonal income patterns. The monetary policy enables the restructuring of credit products to reflect cash flow and payment cycles in the education sector, which helps reduce financial strain during low-admission periods or unforeseen disruptions.
Support for Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) in Education
The policy promotes inclusive credit access for small and medium-sized enterprises, which include privately operated schools, community colleges, and vocational training centers, especially those that serve lower-income populations.
These institutions can benefit from:
-
Simplified loan procedures
-
Reduced collateral requirements
-
Provisions for self-assessed asset valuations (in applicable sectors)
Education Sector’s Role in Productive Lending
While the policy primarily emphasizes productive sectors like agriculture and small industries, education is implicitly included under the productive service sectors. Therefore, banks and financial institutions are encouraged to extend loans to educational businesses that contribute to human capital development and long-term national productivity.